We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Ultrasound: Lungs
From WikEM
(Redirected from Lung ultrasound)
Contents
Technique
- Use vascular probe
- Can use curvilinear or phase probe, but will need to decrease depth
- Place the probe vertically (marker toward head) over the 2nd intercostal space at the midclavicular line
- Adjust your view in order to see a rib on each side of the screen (designated by rib shadow)
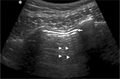
- Look between the ribs for "lung sliding"
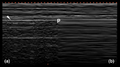
- To document sliding on a single image, use M mode ("waves on a beach")
- Can continue to evaluate each intercostal space for sliding if needed
Pneumothorax
- No lung sliding seen (not specific for pneumothorax)
- May also identify "lung point": distinct point where you no longer see lung sliding (pathognomonic)
- Evaluate other intercostal spaces because pneumothorax may only be seen in least dependent area of thorax
Pulmonary edema
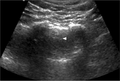
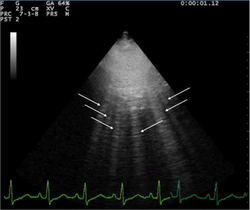
- A lines and B lines
- A lines:
- Appear as horizontal lines
- Indicate dry interlobular septa.
- Predominance of A lines has 90% sensitivity, 67% specificity for pulmonary artery wedge pressure <= 13mm Hg
- A line predominance suggests that intravenous fluids may be safely given without concern for pulmonary edema
- B lines ("comets"):
- White lines from the pleura to the bottom of the screen
- Highly sensitive for pulmonary edema, but can be present at low wedge pressures
- A lines:
BLUE (Bedside Lung Ultrasound in Emergency) Protocol[1]
- Predominant A lines + lung sliding = Asthma/COPD
- Multiple predominant B lines anteriorly with lung sliding = Pulmonary Edema
- Normal anterior profile + DVT= PE
- Anterior absent lung sliding + A lines + lung point = Pneumothorax (PTX)
- Anterior alveolar consolidations, anterior diffuse B lines with abolished lung sliding, anterior asymmetric interstitial patterns, posterior consolidations or effusions with out anterior diffuse B lines = Pneumonia
Further Reading
References
- ↑ ../docss/BLUELung.pdf Relevance of Lung Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure - The BLUE Protocol