Preventing Repeat Teen Births graphics
Infographics for Preventing Repeat Teen Births
Teen Repeat Births
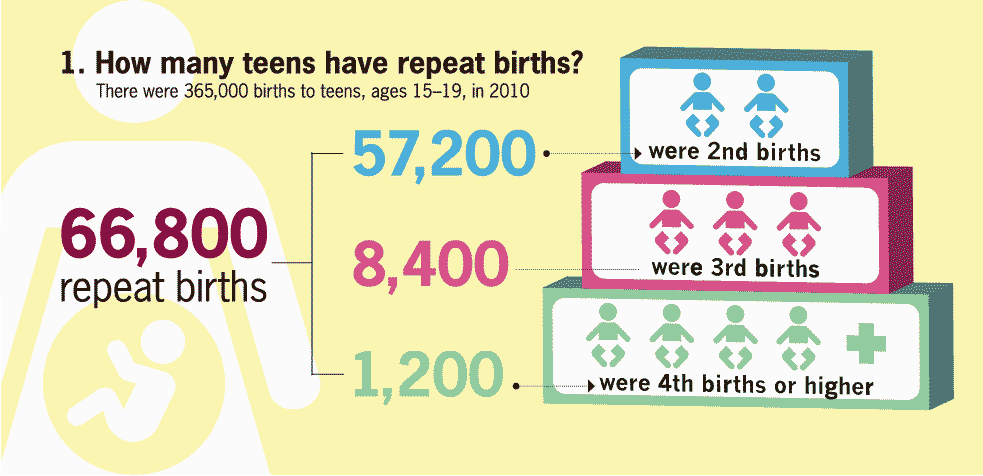
How many teens have repeat births?
SOURCE: National Vital Statistics System, teens, ages 15–19, 2010
Graphic 1: How many teens have repeat births?
There were 365,000 births to teens, ages 15-19, in 2010. Of those, 66,800 were repeat births. 57,200 were 2nd births, 8,400 were 3rd births, and 1,200 were 4th births or higher.
States with Highest Rates
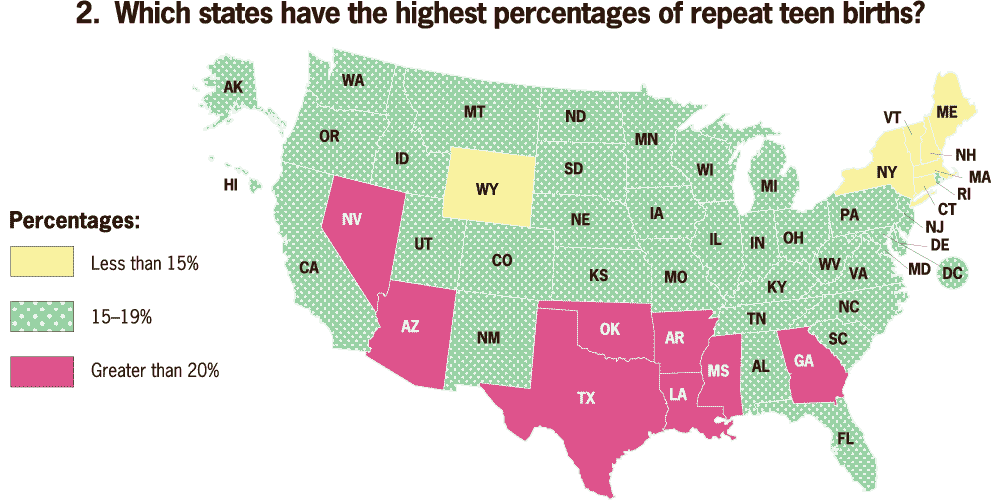
Which states have the highest percentages of repeat teen births?
SOURCE: National Vital Statistics System, teens, ages 15–19, 2010
Graphic 2: Which states have the highest percentages of repeat teen births?
The percentage of teens reporting using the most effective methods of birth control after they gave birth varies geographically. It ranges from 50% in Colorado to 7% in New York State.
Effective Birth Control
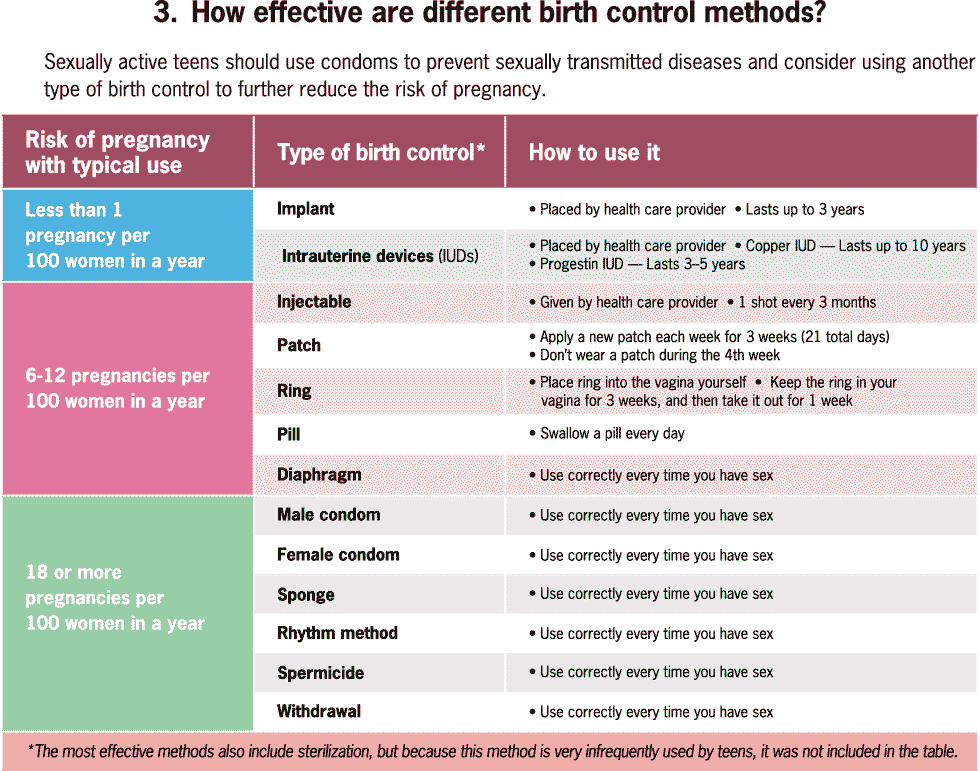
Graphic: How many teens have repeat births?
SOURCE: Adapted from Trussell J in Contraceptive Technology, 2011, and FDA Office of Women’s Health Birth Control Guide [PDF – 921KB]
Graphic 3: How effective are different birth control methods?
This chart depicts the risk of pregnancy with typical use of different types of birth control and how to use them. With implants and Intrauterine devices (IUDs) the risk is less than 1 pregnancy per 100 women in a year, are long acting and are placed by a health care provider. With injectable, patch, ring, pill and diaphragm birth control the risk is typically 6-12 pregnancies per 100 women in a year, have variable lengths and way they are used. With male and female condom, sponge, rhythm method, spermicide and withdrawal, the risk is typically 18 or more pregnancies per 100 women in a year and these must be used correctly every time you have sex.
| Risk of pregnancy with typical use | Type of birth control* | How to use it |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 1 pregnancy per 100 women in a year | Implant |
|
| Intrauterine devices (IUDs) |
|
|
| 6-12 pregnancies per 100 women in a year | Injectable |
|
| Patch |
|
|
| Ring |
|
|
| Pill |
|
|
| Diaphragm |
|
|
| 18 or more pregnancies per 100 women in a year | Male condom |
|
| Female condom |
|
|
| Sponge |
|
|
| Rhythm method |
|
|
| Spermicide |
|
|
| Withdrawal |
|
*The most effective methods also include sterilization, but because this method is very infrequently used by teens, it was not included in the table.
SOURCE: Adapted from Trussell J in Contraceptive Technology, 2011, and FDA Office of Women’s Health Birth Control Guide. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/ForConsumers/ByAudience/ForWomen/FreePublications/UCM282028.pdf
- Page last reviewed: April 2, 2013
- Page last updated: April 2, 2013
- Content source:
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health
- Page maintained by: Office of the Associate Director for Communications (OADC)


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir