What Is Breast Cancer?
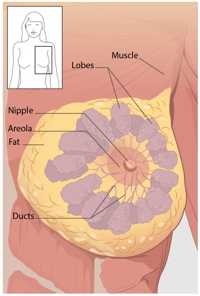
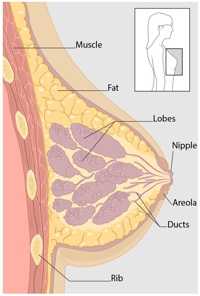
Click to see larger diagrams of the anterior view and cross-section view of the breast.
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
Kinds of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are—
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
There are several other less common kinds of breast cancer, such as Paget’s disease, medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a breast disease that may lead to breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts, and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
- Page last reviewed: July 25, 2017
- Page last updated: September 27, 2017
- Content source:



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir