Vulnerability Management Life Cycle
The Vulnerability Management Life Cycle is intended to allow organizations to identify computer system security weaknesses; prioritize assets; assess, report, and remediate the weaknesses; and verify that they have been eliminated.
In computer security, a vulnerability is a security flaw or weakness that allows an intruder to reduce a system’s information assurance. A vulnerability requires three elements: a system weakness, an intruder’s access to the weakness, and the intruder’s ability to exploit the weakness using a tool or technique.
Steps in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle
The following diagram illustrates the steps in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle.
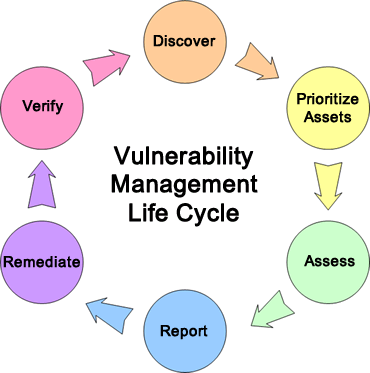
The steps in the Vulnerability Management Life Cycle are described below.
- Discover: Inventory all assets across the network and identify host details including operating system and open services to identify vulnerabilities. Develop a network baseline. Identify security vulnerabilities on a regular automated schedule.
- Prioritize Assets: Categorize assets into groups or business units, and assign a business value to asset groups based on their criticality to your business operation.
- Assess: Determine a baseline risk profile so you can eliminate risks based on asset criticality, vulnerability threat, and asset classification.
- Report: Measure the level of business risk associated with your assets according to your security policies. Document a security plan, monitor suspicious activity, and describe known vulnerabilities.
- Remediate: Prioritize and fix vulnerabilities in order according to business risk. Establish controls and demonstrate progress.
- Verify: Verify that threats have been eliminated through follow-up audits.
- Page last reviewed: January 13, 2015
- Page last updated: January 13, 2015
- Content source:
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir