How to Reduce Indoor Tanning Among Minors
At the federal level—
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulates indoor tanning devices as both medical devices and radiation-emitting electronic products.28
- The Federal Trade Commission investigates false, misleading, and deceptive advertising claims about indoor tanning.29
- The Internal Revenue Service collects a 10% tax on indoor tanning services.30, 31
- CDC and other federal agencies provide evidence-based information about the harms of indoor tanning and the effectiveness of interventions to reduce or prevent these harms.32
Efforts to prevent the harms caused by indoor tanning also are underway at the state and local levels. An overview of state-level indoor tanning policies shows how policies vary across states. Our understanding of which strategies are most effective continues to grow.33 Evidence suggests that the following strategies may be most successful.
Restrictions on Access
Restrictions on use by minors. Indoor tanning at any age increases the risk of getting skin cancer, but is particularly risky for young people.18, 34 Laws restricting indoor tanning among minors have been put into effect in many states and localities across the country. These laws typically take the form of parental consent laws, parental accompaniment laws, or age restrictions (see Box 1 below). Studies have found mixed results with regard to compliance with indoor tanning laws.35–40 Emerging evidence suggests that restrictions on use by minors, particularly those that include age restrictions, may be effective in reducing indoor tanning among minors.32
Box 1. Types of Laws Restricting Indoor Tanning Access Among Minors
Age restrictions: Indoor tanning is prohibited for minors under a certain age.
Parental accompaniment: Parents must accompany minors under a certain age when they tan indoors.
Parental consent: Parents must provide written consent before a child under a certain age can tan indoors.
Restrictions on unsupervised indoor tanning. Unsupervised tanning beds are sometimes available in locations such as gyms and apartment complexes. Unsupervised indoor tanning makes policy enforcement difficult and may hinder efforts to protect minors from the harms of indoor tanning.41
Enforcement
- Routine inspection of tanning facilities and equipment is the first step toward ensuring that policies are enforced.42 State or local health agencies are generally responsible for this enforcement.42
- Fines for policy violations may increase the likelihood of compliance.42, 43 The revenue from fines may be invested in future efforts to support continued enforcement over time.42
Restrictions on Misleading Advertisements
Product marketing has a powerful effect on behaviors and social norms. Advertisements that claim indoor tanning is safe or risk-free are false and misleading.44, 45 Research has shown that children and teens can be influenced easily by these marketing strategies and may not understand the long-term health risks associated with indoor tanning.46
A Comprehensive Approach
Evidence and examples from a variety of fields suggest that a comprehensive approach addressing determinants of health at multiple levels, from individual-level influences to broad contextual factors, may be most successful in improving health-related behaviors (See Figure 1 below).47–50 Such an approach requires collaboration and coordination across many sectors at the national, state, and local levels. Beyond legislative approaches, strategies to reduce indoor tanning among minors may also include individual-focused interventions such as messages tailored for specific audiences; activities that involve parents, doctors, and schools; and mass media campaigns.51 A comprehensive approach also requires that efforts be assessed, monitored, and evaluated to track and measure the short- and long-term effects. Evaluation results can be used to identify which interventions are most effective and sustainable and to guide future prevention efforts. The MPOWER model has been successfully used in tobacco control and provides one potential model for addressing indoor tanning in a comprehensive way.22
Figure 1. Action Model to Achieve Healthy People 2020 Overarching Goals49
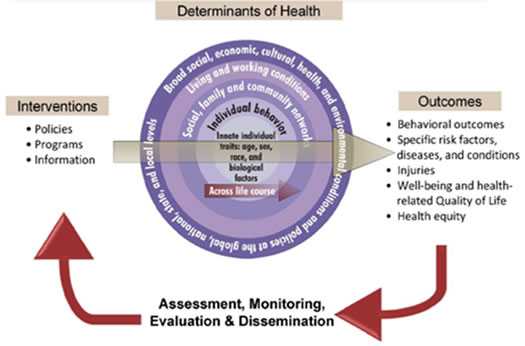
The Action Model to Achieve Healthy People 2020 goals shows that a feedback loop of intervention, assessment, and dissemination of evidence and best practices would enable achievement of Healthy People 2020 goals. Interventions such as policies, programs, and information affect the determinants of health at multiple levels (for example, individual; social, family, and community; living and working conditions; and broad social, economic, cultural, health, and environmental conditions) to improve outcomes. The results of such interventions can be demonstrated through assessment, monitoring, and evaluation. Through dissemination of evidence-based and best practices, these findings would feed back to intervention planning to identify effective prevention strategies in the future.
- Page last reviewed: April 26, 2017
- Page last updated: January 13, 2015
- Content source:
- Maintained By:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir