SARS (10 Years After)
[särz]

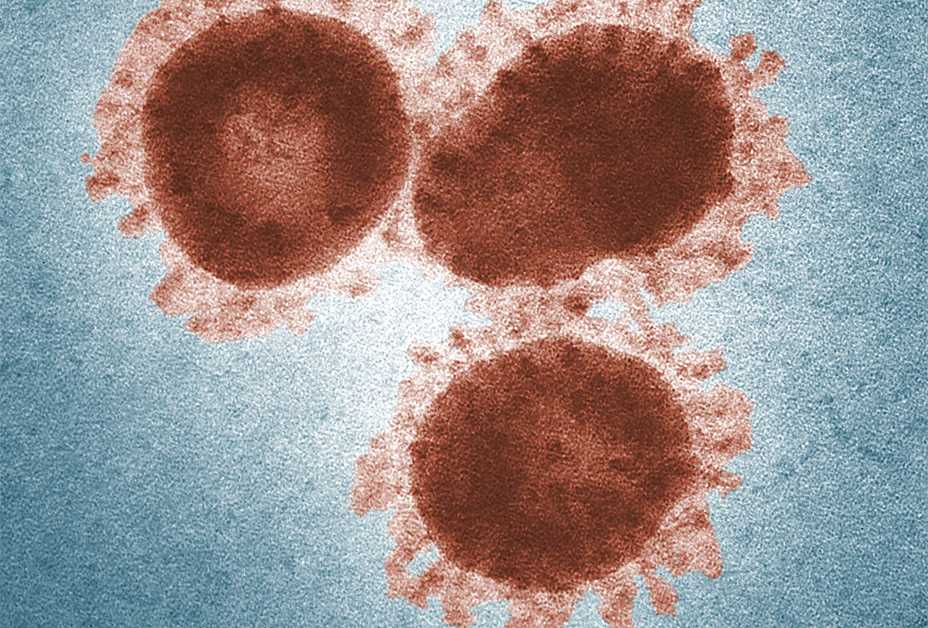
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) is a respiratory illness that affected many people worldwide in 2003. It was caused by a coronavirus, called SARS-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV). SARS was first reported in Asia in February 2003. The illness spread to 29 countries, where 8,096 people got SARS and 774 of them died. The SARS global outbreak was contained in July 2003. Since 2004, there have not been any known cases of SARS reported anywhere in the world.
Quiz
Key Facts
- SARS was caused by a new coronavirus that had never been found in people before.
- In 2003, a total of 8,096 people in 29 countries got SARS and 774 of them died.
- Only eight people in the United States got SARS. None of them died.
- Health professionals around the world worked together to successfully contain the outbreak in 2003.
- In six months, the global SARS outbreak cost the world an estimated $40 billion.
Media
Prevention Tips
-
Wash your hands often with soap and water for 20 seconds, and help young children do the same.
-
Cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you cough or sneeze, then throw the tissue in the trash.
-
Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.
-
Avoid close contact, such as kissing, or sharing cups or eating utensils, with sick people.
-
Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as toys and doorknobs.
- Page last reviewed: March 3, 2016
- Page last updated: March 3, 2016
- Content source:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Page maintained by: Office of Associate Director of Communication, Division of Public Affairs


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir