Content on this page was developed during the 2009-2010 H1N1 pandemic and has not been updated.
- The H1N1 virus that caused that pandemic is now a regular human flu virus and continues to circulate seasonally worldwide.
- The English language content on this website is being archived for historic and reference purposes only.
- For current, updated information on seasonal flu, including information about H1N1, see the CDC Seasonal Flu website.
Prevention Of Pneumococcal Infections Secondary To Seasonal And 2009 H1N1 Influenza Viruses Infection
November 10, 2009 11:00 AM ET
Pneumococcal Disease Complicating Influenza
Influenza predisposes individuals to developing bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. During each of the influenza pandemics of the 20th century, secondary bacterial pneumonia was a frequent cause of illness and death and Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) was reported as the most common etiology. These findings also apply to seasonal influenza.
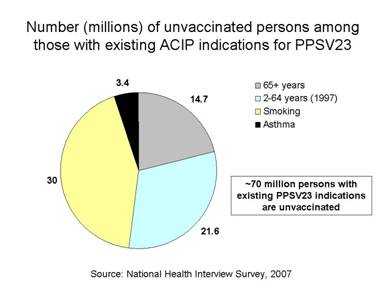
S. pneumoniae remains a leading cause of vaccine-preventable illness and death in the United States. Recently, pneumococcal infections have been identified as an important complication in severe and fatal cases of 2009 H1N1 influenza virus infection. Importantly however, approximately 70 million persons with existing pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) indications (Table) are unvaccinated (National Health Interview Survey, 2007).
Pneumococcal Vaccines
During the 2009-2010 influenza season, pneumococcal vaccines can be useful in preventing secondary pneumococcal infections and reducing illness and death among those infected with influenza viruses. Currently, a pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) is available for prevention of pneumococcal disease among adults and children 2 through 64 years who are at increased risk for pneumococcal disease. All children less than 5 years of age should continue to receive pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) according to existing recommendations.
Use of PPSV during the 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic
CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends a single dose of PPSV for all people 65 years of age and older and for persons 2 through 64 years of age with certain high-risk conditions (Table). Most people in these groups are at increased risk of pneumococcal disease as well as serious complications from influenza viruses infections. A single revaccination at least five years after initial vaccination is recommended for people 65 years and older who were first vaccinated before age 65 years. A single revaccination is also recommended as well as for people at highest risk of disease, such as those who have functional and anatomical asplenia, and those who have HIV infection, AIDS or malignancy and have at least five years elapsed from receipt of first vaccination.
All people who have existing indications for PPSV should continue to be vaccinated according to current ACIP recommendations during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic. Special emphasis should be placed on vaccinating people 2 through 64 years who have established high-risk conditions for pneumococcal disease; PPSV coverage among this group is low and this group may be more likely to develop secondary bacterial pneumonia after an influenza infection.
Use of PPSV among people without current indications for vaccination is not recommended at this time.
Simultaneous Administration of Pneumococcal (PPSV) and Influenza Vaccines
Pneumococcal vaccine can be given at any time during the year and may be given at the same time as influenza vaccine. Visits for seasonal and 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccination provide a convenient time to evaluate patients for the need for pneumococcal vaccination. Persons who cannot remember if they’ve ever had pneumococcal vaccine should be still be vaccinated.
Get email updates
To receive weekly email updates about this site, enter your email address:
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
1600 Clifton Rd
Atlanta, GA 30333 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348 - Contact CDC-INFO


