Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
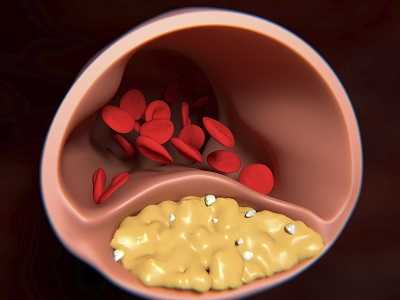
Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque buildup in the wall of the arteries that supply blood to the heart (called coronary arteries). Plaque is made up of cholesterol deposits. Plaque buildup causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease in the United States. For some people, the first sign of CAD is a heart attack. You and your health care team may be able to help you reduce your risk for CAD.
Causes of CAD
CAD is caused by plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart (called coronary arteries) and other parts of the body. Plaque is made up of deposits of cholesterol and other substances in the artery. Plaque buildup causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time, which could partially or totally block the blood flow. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Too much plaque buildup and narrowed artery walls can make it harder for blood to flow through your body. When your heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood, you may have chest pain or discomfort, called angina. Angina is the most common symptom of CAD.
Over time, CAD can weaken the heart muscle. This may lead to heart failure, a serious condition where the heart can’t pump blood the way that it should. An irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, also can develop.
Diagnosing CAD
To find out your risk for CAD, your health care team may measure your blood pressure, cholesterol, and sugar levels. Being overweight, physical inactivity, unhealthy eating, and smoking tobacco are risk factors for CAD. A family history of heart disease also increases your risk for CAD. If you’re at high risk for heart disease or already have symptoms, your doctor can use several tests to diagnose CAD.
| Test | What it Does |
|---|



 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir