Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
Tracking Progress Toward Global Polio Eradication --- Worldwide, 2009--2010
Since the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) began in 1988 (1), progress has been tracked by 1) surveillance comprised of detection and investigation of cases of acute flaccid paralysis (AFP), coupled with environmental surveillance (sewage testing) in selected areas, and 2) timely testing of fecal specimens in accredited laboratories to identify polioviruses. The sensitivity of AFP case detection and the timeliness of AFP investigations are monitored with performance indicators. Polioviruses are isolated and characterized by the Global Polio Laboratory Network (GPLN) (2). This report assesses the quality of polio surveillance and the timeliness of poliovirus isolation reporting and characterization worldwide during 2009--2010. During that period, 77% of countries affected by wild poliovirus (WPV) met national performance standards for AFP surveillance; underperforming subnational areas were identified in two of four countries with reestablished WPV transmission and in 13 of 22 countries with WPV outbreaks. Targets for timely GPLN reporting of poliovirus isolation results were met in five World Health Organization (WHO) regions in 2009 and in four of six regions in 2010; targets for timely poliovirus characterization were met in four WHO regions in 2009 and in five regions in 2010. Monitoring of surveillance performance indicators at subnational levels continues to be critical to identifying surveillance gaps that might allow WPV circulation to be missed in certain areas or subpopulations. To achieve polio eradication, efforts are needed to further strengthen AFP surveillance, implement targeted environmental surveillance, and ensure that GPLN quality is maintained.
AFP Surveillance
AFP surveillance, which detects paralytic illness of many causes, 1) identifies areas in countries with WPV circulation where polio cases might go undetected and supplementary immunization activities (SIAs)* are needed, 2) detects WPV circulation in previously polio-free areas, and 3) helps confirm the absence of WPV circulation in countries with only valid nonpolio AFP (NPAFP) test results. The quality of AFP surveillance is monitored with performance indicators for detection sensitivity and investigation timeliness established by WHO. Sensitivity is measured by the annual rate of AFP cases with adequate stool specimens testing negative for WPV among children aged <15 years (the NPAFP rate); investigation timeliness is measured by the proportion of AFP cases in which two adequate stool specimens were taken ≤14 days after onset and properly transported to an accredited GPLN laboratory (the specimen adequacy proportion).†
Among the six WHO regions, the Region of the Americas was certified polio-free in 1998, the Western Pacific Region in 2000, and the European Region in 2002. During 2009--2010, Afghanistan, India, Nigeria, and Pakistan remained endemic with indigenous WPV transmission. WPV transmission in Angola, Chad, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), and Sudan, once polio-free countries, was reestablished after importation before 2009.
During 2009--2010, the three WHO regions certified as polio-free maintained overall AFP surveillance sensitivity at ≥1 NPAFP case per 100,000 children, the WHO-specified national target, except for the European Region in 2009 (Table 1). In the three polio-endemic regions, an operational target of a national NPAFP rate of ≥2 cases per 100,000 children has been set for countries reporting WPV and for neighboring countries at risk for WPV transmission (3); this target was met in 27 (90%) of 30 polio-affected countries in both 2009 and 2010 (Table 1). Following WPV importation into the European Region in 2010, two outbreak-affected countries raised their NPAFP target rate to ≥2 from ≥1 in 2009. All WHO regions, except for the Americas in 2009, maintained an overall proportion of ≥80% AFP cases with adequate stool specimens, the WHO-specified national target (Table 1). The proportion of AFP cases with adequate stool specimens met the national target of ≥80% in 23 (77%) of the polio-affected countries in both 2009 and 2010 (Table 1).
Surveillance quality varied substantially at subnational levels; 22 (73%) polio-affected countries achieved an NPAFP rate of ≥2 in ≥80% of subnational areas (states/provinces) in both years (Table 1, Figure). In only 18 (60%) countries was the standard of ≥80% of AFP cases having adequate specimens achieved in ≥80% of states/provinces in both years (Table 1, Figure). Analysis in relation to population distribution showed that only 15 (50%) of 30 polio-affected countries met both these standards in subnational areas: nine of 22 countries with outbreaks, all four countries with endemic WPV circulation, and two (Angola and Sudan) of the four countries with reestablished transmission. One concern is the clustering of states/provinces with suboptimal surveillance performance indicators within polio-affected countries or their neighbors and at country borders, such as Uganda/Kenya (Figure).
Global Polio Laboratory Network
The WHO-coordinated GPLN, which consists of 146 laboratories in 97 countries, guides program activities through timely isolation and characterization of polioviruses (PVs) as Sabin-like vaccine-related PV, vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) or WPV by intratypic differentiation (ITD), and characterization of VDPVs and WPVs through comprehensive genomic sequencing. A revised laboratory algorithm introduced in 2008 set a goal of PV detection in ≥80% of specimens within 14 days following specimen receipt.§ The introduction of real-time polymerase chain reaction tools into reference laboratories enables characterization of a virus by ITD within 7 days (4).
Targets for timely reporting of poliovirus isolation results were met in four of six WHO regions in 2010, compared with five in 2009 (Table 2). Delays in 2010 in the European Region in part resulted from a large number of specimens processed in batches during a WPV outbreak that involved four countries (5). Allowing for case detection, investigation, and transport of specimens, the target is reporting of ITD results within 60 days of paralysis onset for ≥80% of specimens. Five WHO regions provided ≥80% of ITD results within the 60-day target in 2010, compared with four in 2009 (Table 2). Difficulties in international specimen transport contributed to failure to meet the ITD target in the African Region.
GPLN tested 194,374 stool specimens from investigations of AFP cases in 2010, a 9% increase in workload compared with 178,968 specimens in 2009. Additionally, testing of samples and specimens from non-AFP sources (e.g., sewage samples and specimens from healthy children) increased 14.6% to 17,438 in 2010 from 15,215 in 2009.
PV isolates are divided into three serotypes: type 1, type 2, and type 3. Isolates are divided further into three categories, based on the extent of VP1 nucleotide sequence divergence from the corresponding Sabin OPV strain¶**: 1) Sabin vaccine-related PVs, 2) VDPVs, and 3) WPVs. A total of 8,902 PVs (including 1,679 WPV isolates) were detected in 2010 from AFP specimens, an 8% decrease from 9,706 (including 2,963 WPV isolates) detected in 2009. Additionally, non-AFP sources yielded 151 WPVs in 2010 and 160 WPVs in 2009. During 2009--2010, 14,263 vaccine-related viruses from AFP cases were screened for VDPVs; 297 (2.1%) were characterized as VDPVs (Table 2).
Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the VP1 region of the viral genome is used to investigate genetic and transmission links among WPV isolates, track international spread (2,5), and estimate duration of circulation (6). Continued transmission during 2009--2010 of the four remaining WPV genotypes†† was confirmed. Sequence analysis provided virologic evidence that AFP surveillance generally meeting national and in some cases subnational standards had missed some chains of WPV transmission in Angola, Chad, DRC, Nigeria, and Pakistan (6,7).
Environmental Surveillance
Community transmission of WPV has been monitored through testing of sewage samples from populated areas for 70 years in several developed countries (8) and also has been implemented in selected areas of developing countries. Weekly sampling in Mumbai, India, during 2009 detected multiple WPVs (where no specimens from AFP cases had been WPV positive) closely related to WPVs circulating in several other areas of India (9); testing in 2010 produced a single WPV-positive result in November. Sampling in Delhi was begun in May 2010, producing WPV positives through August, but none since. In Pakistan, monthly environmental sampling began in six cities in 2010; a total of 80 of 157 samples tested positive for WPV, including samples collected in Karachi and Lahore, where no specimens from AFP cases had been WPV positive. Genomic sequencing of isolates indicated that multiple chains of transmission were ongoing at these sites.
Reported by
Polio Eradication Dept, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. Div of Viral Diseases; Global Immunization Div;* National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC. *Corresponding contributor: IU Ogbuanu, MD, Global Immunization Div, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (EIS Officer), CDC, 404-639-8757, ige2@cdc.gov.
Editorial Note
AFP surveillance (supplemented by targeted environmental surveillance), virologic testing, and genomic sequencing analysis guide GPEI activities. Standardized case detection, field investigation, and laboratory methods provide the comparability across countries and WHO regions needed to monitor progress towards polio eradication. GPLN performance in 2009 and 2010 has continued to improve, even with increases in workload. Over 90% of isolation and ITD results have been reported within the target periods, each of which have been reduced by half since introduction of revised laboratory algorithms and methods (2,4). By providing results more promptly, the ability to implement well-timed response SIAs has been strengthened.
Supplementary environmental surveillance has been valuable in India, where low-level transmission has occurred, as well as in Pakistan, where subnational AFP surveillance indicators have met targets but virologic analysis indicated major gaps in detection. Currently, plans are being made to implement environmental sampling in Nigeria during 2011. As fewer circulating WPVs are detected, the role of environmental sampling will increase, in addition to its use for detection of potential VDPVs.
Continuing indigenous and reestablished transmission and recent outbreaks in previously polio-free countries highlight the necessity to continuously monitor AFP surveillance indicators everywhere. Timely investigation and specimen collection has declined for some key reservoir countries (Chad and DRC). NPAFP case detection and timely specimen collection have declined in some countries of polio-free WHO regions over the 10 or more years since certification (1). Large outbreaks can result when standard timeframes and procedures in investigation, transport, and testing are not followed, as illustrated by recent outbreaks in Tajikistan and the Republic of the Congo (5,10). In addition, substantial surveillance deficiencies exist at subnational levels in many countries, including some where national surveillance indicators have met operational targets.
Among countries currently affected by polio, surveillance gaps discovered by virologic evidence of missed chains of transmission might have resulted from lapses in 1) AFP detection in certain local areas or among certain subpopulations (e.g., migrants), 2) AFP case investigation, and 3) specimen collection or transport. To stay on target to meet WPV transmission interruption targets of the 2010--2012 GPEI strategic plan and minimize the extent of any additional outbreaks, efforts should be made to strengthen polio surveillance at each subnational level and maintain and monitor high polio vaccination coverage at all administrative levels.
References
- CDC. Progress toward interruption of wild poliovirus transmission---worldwide, 2009. MMWR 2010;59:545--50.
- CDC. Laboratory surveillance for wild and vaccine-derived polioviruses---worldwide, January 2008--June 2009. MMWR 2009;58:950--4.
- World Health Organization. Conclusions and recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Poliomyelitis Eradication, Geneva, 11--12 October 2005. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2010;80:410--6.
- Kilpatrick DR, Yang CF, Ching K, et al. Rapid group-, serotype-, and vaccine strain-specific identification of poliovirus isolates by real-time reverse transcription--PCR using degenerate primers and probes containing deoxyinosine residues. J Clin Microbiol 2009;47:1939--41.
- CDC. Outbreaks following wild poliovirus importations---Europe, Africa, and Asia, January 2009--September 2010. MMWR 2010;59:1393--9.
- CDC. Progress toward interrupting wild poliovirus circulation in countries with reestablished transmission---Africa, 2009--2010. MMWR 2011;60:306--11.
- CDC. Progress toward poliomyelitis eradication---Nigeria, January 2009--June 2010. MMWR 2010;59:802--7.
- Trask JD, Paul JR. Periodic examination of sewage for the virus of poliomyelitis. J Exp Med 1942;75:1--6.
- Deshpande JM, Shetty SJ, Siddiqui ZA. Environmental surveillance system to track wild poliovirus transmission. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003,69:2919--27.
- CDC. Poliomyelitis outbreak---Republic of the Congo, September 2010--February 2011. MMWR 2011;60:312--3.
* Mass campaigns conducted for a brief period (days to weeks), during which 1 dose of oral poliovirus vaccine is administered to all children aged <5 years, regardless of vaccination history.
† Additional information available at http://www.who.int/vaccines-documents/docspdf06/843.pdf.
§ Additional information available at http://www.polioeradication.org/resourcelibrary/gplnpublications.aspx.
¶ For PV types 1 and 3, 10 or more VP1 nucleotide differences from the respective Sabin PV; as of 2010, for PV type 2, six or more VP1 nucleotide differences from Sabin type 2 PV.
** Report of the 2010 Informal Consultation of The Global Polio Laboratory Network, available at http://www.polioeradication.org/resourcelibrary/gplnpublications.aspx.
†† Designated as West Africa-B (WEAF-B) WPV1, WEAF-B WPV3, South Asia (SOAS) WPV1, and SOAS WPV3, each containing virus isolates with >85% VP1 nucleotide similarity.
What is already known on this topic?
To interrupt wild poliovirus (WPV) transmission, the Global Polio Eradication Initiative relies on surveillance for acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) and investigation, followed by virologic testing of specimens and genomic sequencing analysis of polioviruses. Laboratory testing of stool specimens from AFP cases enables them to be characterized as nonpolio AFP or WPV cases.
What is added by this report?
AFP surveillance activities are suboptimal in many areas. During 2009--2010, 77% of polio-affected countries met national performance standards for AFP surveillance. Surveillance quality varied substantially at subnational (state/province) levels; underperforming subnational areas were found in 15 of 30 polio-affected countries during 2009--2010.
What are the implications for public health practice?
National surveillance indicators can mask subnational AFP surveillance weaknesses; monitoring performance indicators at subnational levels is critical for identifying gaps that could allow WPV circulation to be missed in areas or subpopulations. Efforts should be made to strengthen subnational AFP surveillance to detect low-level WPV transmission and promptly identify importation into previously polio-free countries.
FIGURE. Combined performance indicators for the quality of acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) surveillance* in subnational areas (states/provinces) of 30 current or recently polio-affected countries and neighboring countries in Africa, 2010†
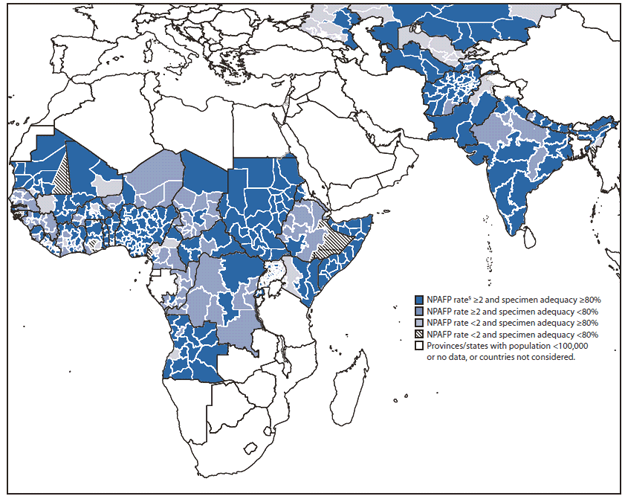
Abbreviation: NPAFP = nonpolio AFP.
* The Global Polio Eradication Initiative 2010--2012 strategic plan sets the following targets for countries with current or recent wild poliovirus (WPV) transmission and their states/provinces: 1) a NPAFP detection rate of ≥2 cases per 100,000 persons aged <15 years and 2) adequate stool specimen collection from ≥80% of AFP cases with adequate specimens, which is defined as two specimens collected ≥24 hours apart, both within 14 days of paralysis onset, shipped on ice or frozen ice packs, and arriving in good condition (without leakage or desiccation) at a World Health Organization--accredited laboratory.
† Data are for AFP cases with onset during 2010, reported as of March 15, 2011.
§ Per 100,000 persons aged <15 years.
Alternate Text: The figure above shows combined performance indicators for the quality of acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) surveillance in subnational areas (states/provinces) of 30 current or recently polio-affected countries and neighboring countries in Africa in 2010. In only 18 countries was the standard of ≥80% of AFP cases having adequate specimens achieved in ≥80% of states/provinces in both years.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents.
This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version.
Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr)
and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371;
telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to
mmwrq@cdc.gov.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


