Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
QuickStats: Percentage of Adults Aged ≥25 Years Reporting Fair or Poor Health,* by Age Group and Income§ --- National Health Interview Survey, United States, 2007--2009†
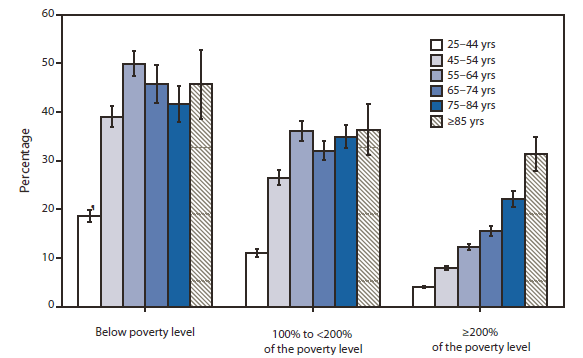
* Respondents were asked to assess their own health and that of family members living in the same household as excellent, very good, good, fair, or poor. Data are presented only for respondents aged ≥25 years.
§ Family income is expressed as a percentage of the federal poverty level and grouped into three categories. Family income was imputed when information was missing by using multiple imputation methodology.
† Estimates are based on household interviews of a sample of the noninstitutionalized U.S. civilian population. Denominators for each category exclude persons for whom data were missing.
¶ 95% confidence interval.
During 2007--2009, the percentage of adults who reported their health as fair or poor increased with age group among those in families with incomes ≥200% of the poverty level, from 4.1% among persons aged 25--44 years to 31.4% among persons aged ≥85 years. However, among those in families with lower incomes, the percentage reporting fair or poor health increased with age only until age 55--64 years, with those aged ≥65 years no more likely to report fair or poor health than those aged 55--64 years. For each age group, persons in families whose income was below poverty level were most likely to report fair or poor health.
Sources: National Health Interview Survey, 2007--2009 data. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm.
CDC. Health Data Interactive. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hdi.htm.
Alternate Text: The figure above shows the percentage of adults aged ≥25 years reporting fair or poor health, by age group and income in the United States during 2007-2009. During 2007-2009, the percentage of adults who reported their health as fair or poor increased with age group among those in families with incomes ≥200% of the poverty level, from 4.1% among persons aged 25-44 years to 31.4% among persons aged ≥85 years. However, among those in families with lower incomes, the percentage reporting fair or poor health increased with age only until age 55-64 years, with those aged ≥65 years no more likely to report fair or poor health than those aged 55-64 years.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents.
This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version.
Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr)
and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S.
Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371;
telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to
mmwrq@cdc.gov.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


