Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
QuickStats: Percentage of Adults Aged 20--64 Years with Hypertension Whose Condition Was Undiagnosed,* by Health Insurance Status† and Age Group --- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, United States, 2005--2008
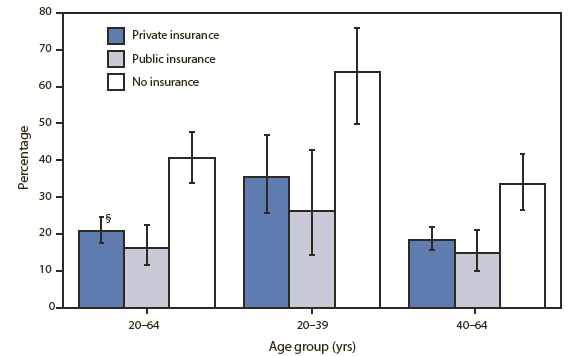
* Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg or currently taking medication to lower blood pressure, based on positive responses to the following questions: "Because of your high blood pressure/hypertension have you ever been told to take prescribed medicine?" and "Are you now taking a prescribed medicine?" Undiagnosed hypertension was a finding of hypertension and a negative response to the following question: "Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that you had hypertension, also called high blood pressure?"
† Health insurance coverage is at the time of interview. Public coverage includes Medicaid, Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) state-sponsored or other government-sponsored health plan, Medicare (disability), or military health plan (TRICARE, VA, or CHAMP-VA). Persons with both public and private insurance coverage were included in the private coverage category only.
§ 95% confidence interval.
During 2005--2008, among U.S. adults aged 20--64 years with hypertension, 40% of those with no health insurance had hypertension that was undiagnosed, compared with 21% of those with private insurance and 16% of those with public insurance. In the 20--39 years and 40--64 years age groups, undiagnosed hypertension also was more common among persons with no health insurance compared with those with private or public insurance.
Sources: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005--2008 data. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm.
Schober SE, Makuc DM, Zhang C, Kennedy-Stephenson J, Burt V. Health insurance affects diagnosis and control of hypercholesterolemia and hypertension among adults aged 20--64: United States, 2005--2008. NCHS data brief no. 57. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2011. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db57.pdf.
Alternate Text: The figure above shows the percentage of adults aged 20-64 years with hypertension whose condition was undiagnosed, by health insurance status and age group, in the United States during 2005-2008, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. During 2005-2008, among U.S. adults aged 20-64 years with hypertension, 40% of those with no health insurance had hyperten-sion that was undiagnosed, compared with 21% of those with private insurance and 16% of those with public insurance. In the 20-39 years and 40-64 years age groups, undiagnosed hypertension also was more common among persons with no health insurance compared with those with private or public insurance.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. |
All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from typeset documents. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables. An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371; telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices.
**Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to
mmwrq@cdc.gov.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


