Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Extreme Obesity Among Adults: United States, Trends 1960–1962 Through 2009–2010
by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D., Division of Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
PDF Version (284 KB)
Results from the 2009–2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), using measured heights and weights, indicate that an estimated 33.0% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over are overweight, 35.7% are obese, and 6.3% are extremely obese (Table 1). Body mass index (BMI), expressed as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2), is commonly used to classify overweight (BMI 25.0–29.9), obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30.0), and extreme obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 40.0).
One of the national health objectives for the Healthy People 2020 initiative is to reduce the prevalence of obesity among adults by 10.0%, to 30.6%. NHANES 2009–2010 data for adults aged 20 and over suggest an increase in obesity between the late 1980s and today in the United States, with the estimated age-adjusted prevalence moving upward from a previous level of 23.0% in NHANES III (1988–1994) to approximately 36.0% in 2009–2010. Among women, however, no significant change was observed between 1999–2000 and 2009–2010. Among men, there was a significant linear increase between 1999–2000 and 2009–2010, but no significant change between 2005–2006 and 2009–2010. Trends in obesity and overweight prevalence since 1988–1994 are shown in Table 1.
It is possible to examine trends since 1960 among adults aged 20–74 (Table 2). Although the prevalence of obesity among adults aged 20–74 more than doubled between 1976–1980 and 2009–2010, the prevalence of overweight remained stable during the same period (Table 2). The sex-specific trends of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Racial and ethnic disparities in adult obesity
Table 3 shows the estimates in obesity prevalence by race and ethnicity for men and women since NHANES III (1988–1994).
In 2009–2010 and 1988–1994, no significant differences were seen between racial and ethnic groups in the prevalence of obesity among men.
Between 1988–1994 and 2009–2010, the prevalence of obesity among men increased (Figure 3):
- From 20.3% to 36.2% among non-Hispanic white men.
- From 21.1% to 38.8% among non-Hispanic black men.
- From 23.9% to 36.6% among Mexican-American men.
Among women in 2009–2010, non-Hispanic black women (58.5%) were significantly more likely to be obese than non-Hispanic white women (32.2%) and Mexican-American women (44.9%). Mexican-American women were more likely to be obese than non-Hispanic white women. Similar disparities in obesity existed in 1988–1994 when comparing non-Hispanic white women (22.9%) with non-Hispanic black women (38.4%) and Mexican-American women (35.4%). However, in 1988–1994, no significant difference in obesity was observed between non-Hispanic black and Mexican-American women.
Between 1988–1994 and 2009–2010, the prevalence of obesity among women increased (Figure 4):
- From 22.9% to 32.2% among non-Hispanic white women.
- From 38.4% to 58.5% among non-Hispanic black women.
- From 35.4% to 44.9% among Mexican-American women.
NHANES uses a stratified, multistage probability sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized U.S. population. A household interview and a physical examination are conducted for each survey participant. During the physical examination, conducted in a mobile examination center, height and weight are measured as part of a comprehensive set of body measurements. These measurements are taken by trained health technicians, using standardized measuring procedures and equipment. Observations for pregnant women and for persons missing a valid height or weight measurement are not included in the data analysis.
Figures
Figure 1. Trends in overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among men aged 20–74 years: United States, 1960–1962 through 2009–2010
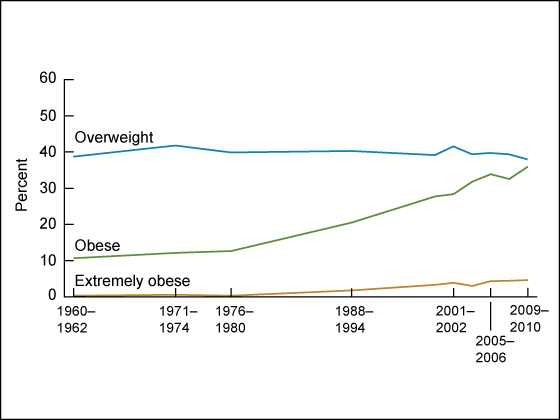
NOTES: Age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. Overweight is a body mass index (BMI) of 25 kg/m2 or greater but less than 30 kg/m2; obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2; and extreme obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 40 kg/m2.
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey I 1960–1962; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) I 1971–1974; NHANES II 1976–1980; NHANES III 1988–1994; NHANES 1999–2000, 2001–2002, 2003–2004, 2005–2006, 2007–2008, and 2009–2010.
Figure 2. Trends in overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among women aged 20–74 years: United States, 1960–1962 through 2009–2010
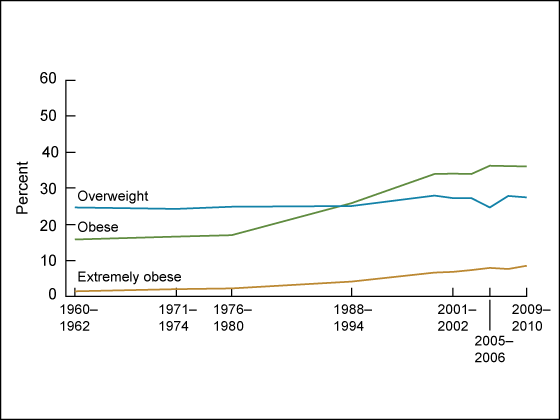
NOTES: Age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. Pregnant females were excluded. Overweight is a body mass index (BMI) of 25 kg/m2 or greater but less than 30 kg/m2; obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2; and extreme obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 40 kg/m2.
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey I 1960–1962; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) I 1971–1974; NHANES II 1976–1980; NHANES III 1988–1994; NHANES 1999–2000, 2001–2002, 2003–2004, 2005–2006, 2007–2008, and 2009–2010.
Figure 3. Prevalence of obesity among men aged 20 years and over, by race and ethnicity: United States, 1988–1994 and 2009–2010
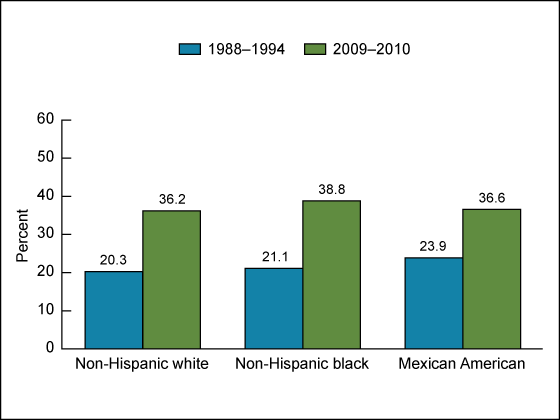
NOTES: Age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Obesity is a body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2.
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III 1988–1994 and NHANES 2009–2010.
Figure 4. Prevalence of obesity among women aged 20 years and over, by race and ethnicity: United States, 1988–1994 and 2009–2010
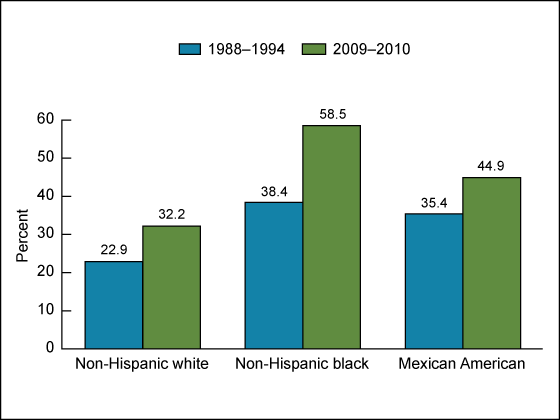
NOTES: Age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Pregnant females were excluded. Obesity is a body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2.
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III 1988–1994 and NHANES 2009–2010.
Tables
Table 1. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among U.S. adults aged 20 and over
| Sample size and weight status |
NHANES III 1988-1994 |
NHANES 1999-2000 |
NHANES 2001-2002 |
NHANES 2003-2004 |
NHANES 2005-2006 |
NHANES 2007-2008 |
NHANES 2009-2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample (n) | 16,235 | 4,117 | 4,413 | 4,431 | 4,356 | 5,550 | 5,926 |
| Total | |||||||
| Overweight | 33.1 | 34.0 | 35.1 | 34.1 | 32.6 | 34.3 | 33.0 |
| Obese | 22.9 | 30.5 | 30.5 | 32.2 | 34.3 | 33.7 | 35.7 |
| Extremely obese | 2.8 | 4.7 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 5.9 | 5.7 | 6.3 |
| Men | |||||||
| Overweight | 40.7 | 39.7 | 42.2 | 39.7 | 39.9 | 40.1 | 38.4 |
| Obese | 20.2 | 27.5 | 27.7 | 31.1 | 33.3 | 32.2 | 35.5 |
| Extremely obese | 1.7 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.4 |
| Women | |||||||
| Overweight | 25.9 | 28.6 | 28.2 | 28.6 | 25.5 | 28.6 | 27.9 |
| Obese | 25.4 | 33.4 | 33.2 | 33.2 | 35.3 | 35.4 | 35.8 |
| Extremely obese | 3.9 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 8.1 |
1Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2.
NOTES: NHANES is National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; BMI is body mass index. Data are age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Crude estimates (not age adjusted) for 2009–2010 are 33.3% overweight, 35.9% obese, and 6.3% extremely obese. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, NHANES.
Table 2. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among U.S. adults aged 20-74
| Sample size and weight status | NHES I 1960-1962 |
NHANES I 1971-1974 |
NHANES II 1976-1980 |
NHANES III 1988-1994 |
NHANES 1999-2000 |
NHANES 2001-2002 |
NHANES 2003-2004 |
NHANES 2005-2006 |
NHANES 2007-2008 |
NHANES 2009-2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample (n) | 6,126 | 12,911 | 11,765 | 14,319 | 3,603 | 3,916 | 3,756 | 3,835 | 4,876 | 5,279 |
| Total | ||||||||||
| Overweight | 31.5 | 32.3 | 32.1 | 32.7 | 33.6 | 34.4 | 33.4 | 32.2 | 33.6 | 32.7 |
| Obese | 13.4 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 23.2 | 30.9 | 31.3 | 32.9 | 35.1 | 34.3 | 36.1 |
| Extremely obese | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 6.6 |
| Men | ||||||||||
| Overweight | 38.7 | 41.7 | 39.9 | 40.3 | 39.2 | 41.5 | 39.4 | 39.7 | 39.4 | 38.0 |
| Obese | 10.7 | 12.1 | 12.7 | 20.5 | 27.7 | 28.3 | 31.7 | 33.8 | 32.5 | 35.9 |
| Extremely obese | *0.3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 3.0 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.6 |
| Women | ||||||||||
| Overweight | 24.7 | 24.3 | 24.9 | 25.1 | 28.0 | 27.3 | 27.3 | 24.7 | 27.9 | 27.5 |
| Obese | 15.8 | 16.6 | 17.0 | 25.9 | 34.0 | 34.1 | 34.0 | 36.3 | 36.2 | 36.1 |
| Extremely obese | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 4.1 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 7.6 | 8.5 |
*Estimate has a relative standard error greater than 30% and less than or equal to 40% and should be used with caution because it does not meet standards of reliability or precision.
1Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2.
NOTES: NHES is National Health Examination Survey; NHANES is National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; BMI is body mass index. Data are age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. NHES included adults aged 18–79, and NHANES I and II did not include individuals over age 74, so trend estimates are based on ages 20–74. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCES: CDC/NCHS, NHES and NHANES.
Table 3. Prevalence of obesity among U.S. adults aged 20 and over, by sex and race and ethnicity, for selected years 1988–1994 through 2009–2010
| Characteristic | NHANES III 1988-1994 | NHANES 1999-2000 | NHANES 2001-2002 | NHANES 2003-2004 | NHANES 2005-2006 | NHANES 2007-2008 | NHANES 2009-2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | |||||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 20.3 | 27.3 | 29.0 | 31.1 | 33.0 | 31.9 | 36.2 |
| Non-Hispanic black | 21.1 | 27.9 | 27.9 | 34.0 | 37.0 | 37.2 | 38.8 |
| Men, Mexican American | 23.9 | 28.9 | 25.9 | 31.6 | 27.0 | 35.8 | 36.6 |
| Women | |||||||
| Non-Hispanic white | 22.9 | 30.1 | 31.2 | 30.2 | 32.9 | 33.0 | 32.2 |
| Non-Hispanic black | 38.4 | 49.5 | 48.2 | 53.9 | 52.9 | 49.4 | 58.5 |
| Mexican American | 35.4 | 39.5 | 37.0 | 42.3 | 42.1 | 45.1 | 44.9 |
NOTES: NHANES is National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Data are age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. Census population using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Obesity is body mass index greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, NHANES.
For more detailed estimates see
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 288(14):1723–7. 2002.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295(13):1549–55. 2006.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, McDowell MA, Flegal KM. Obesity among adults in the United States—No statistically significant change since 2003–2004 [PDF – 366 KB]. NCHS data brief no 1. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2007.
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303(3):235–41. 2010.
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 307(5):491–7. 2012.
This Health E-Stat from NHANES supersedes the earlier versions below.
- Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–1962 through 2007–2008
- Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–62 through 2005–2006
- Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults: United States, 2003–2004
- Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults: United States, 1999–2002
- Page last reviewed: November 6, 2015
- Page last updated: September 13, 2012
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir