Diagnosis & Detection
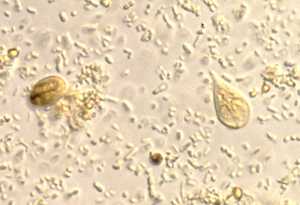
Giardia trophozoites and cysts. Credit: Waterborne Disease Prevention Branch, CDC
Because Giardia cysts can be excreted intermittently, multiple stool collections (i.e., three stool specimens collected on separate days) increase test sensitivity 1. The use of concentration methods and trichrome staining might not be sufficient to identify Giardia because variability in the concentration of organisms in the stool can make this infection difficult to diagnose. For this reason, fecal immunoassays that are more sensitive and specific should be used 2.
Rapid immune-chromatographic cartridge assays also are available but should not take the place of routine ova and parasite examination 2. Only molecular testing (e.g., polymerase chain reaction) can be used to identify the subtypes of Giardia.
References
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Procedures for the recovery and identification of parasites from the intestinal tract; approved guideline. CLSI document M28-A2. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute; 2005.
- Johnston SP, Ballard MM, Beach MJ, Causer L, Wilkins PP. Evaluation of three commercial assays for detection of Giardia and Cryptosporidium organisms in fecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(2):623-6.
- Page last reviewed: July 21, 2015
- Page last updated: July 21, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir