Biology
Causal Agents:
Protozoan hemoflagellates belonging to the complex Trypanosoma brucei. Two subspecies that are morphologically indistinguishable cause distinct disease patterns in humans: T. b. gambiense causes West African sleeping sickness and T. b. rhodesiense causes East African sleeping sickness. (A third member of the complex, T. b. brucei, under normal conditions does not infect humans.)
Life Cycle:
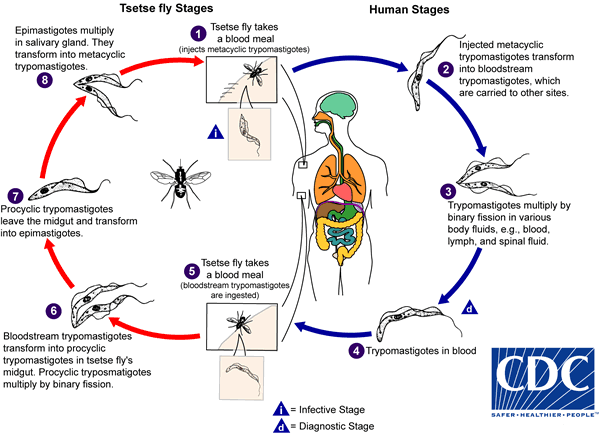
During a blood meal on the mammalian host, an infected tsetse fly (genus Glossina) injects metacyclic trypomastigotes into skin tissue. The parasites enter the lymphatic system and pass into the bloodstream  . Inside the host, they transform into bloodstream trypomastigotes
. Inside the host, they transform into bloodstream trypomastigotes  , are carried to other sites throughout the body, reach other blood fluids (e.g., lymph, spinal fluid), and continue the replication by binary fission
, are carried to other sites throughout the body, reach other blood fluids (e.g., lymph, spinal fluid), and continue the replication by binary fission  . The entire life cycle of African Trypanosomes is represented by extracellular stages. The tsetse fly becomes infected with bloodstream trypomastigotes when taking a blood meal on an infected mammalian host (
. The entire life cycle of African Trypanosomes is represented by extracellular stages. The tsetse fly becomes infected with bloodstream trypomastigotes when taking a blood meal on an infected mammalian host ( ,
,  ). In the fly’s midgut, the parasites transform into procyclic trypomastigotes, multiply by binary fission
). In the fly’s midgut, the parasites transform into procyclic trypomastigotes, multiply by binary fission  , leave the midgut, and transform into epimastigotes
, leave the midgut, and transform into epimastigotes  . The epimastigotes reach the fly’s salivary glands and continue multiplication by binary fission
. The epimastigotes reach the fly’s salivary glands and continue multiplication by binary fission  . The cycle in the fly takes approximately 3 weeks. Humans are the main reservoir for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, but this species can also be found in animals. Wild game animals are the main reservoir of T. b. rhodesiense.
. The cycle in the fly takes approximately 3 weeks. Humans are the main reservoir for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense, but this species can also be found in animals. Wild game animals are the main reservoir of T. b. rhodesiense.
Life cycle image and information courtesy of DPDx.
- Page last reviewed: March 16, 2015
- Page last updated: March 16, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir