

|

|

Volume 1:
No. 4, October 2004
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Inadequate Functional Health Literacy in Spanish as a Barrier to Cervical
Cancer Screening Among Immigrant Latinas in New York City
Samantha Garbers, MPA, Mary Ann Chiasson, DrPH
Suggested citation for this article: Garbers S, Chiasson MA.
Inadequate functional health literacy in Spanish as a barrier to cervical
cancer screening among immigrant Latinas in New York City. Prev Chronic
Dis [serial online] 2004 Oct [date cited]. Available from: URL:
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2004/
oct/03_0038.htm.
PEER REVIEWED
Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to examine the association between inadequate
functional health literacy in Spanish among low-income Latinas aged 40 and older and cervical cancer screening knowledge and behavior.
Methods
Spanish-speaking Latinas aged 40–78 of various nationalities (n = 205) participated
in a study that included a survey on cervical cancer
knowledge and behavior administered in Spanish and the Spanish version of the Test of Functional Health
Literacy in Adults.
Results
Compared to those with adequate and marginal health literacy, women with
inadequate functional health literacy in Spanish were significantly less likely
to have ever had a Papanicolaou (Pap) test (odds ratio, 0.12; 95% confidence
interval [CI], 0.04-0.37) or in
the last three years (odds ratio, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.18-0.68) and were
significantly more likely to have had their last Pap test at a local public
hospital (odds ratio, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.18-4.97). Even when controlling for other
factors, women with inadequate health literacy were 16.7 times less likely
(adjusted odds ratio, 0.06; 95% CI, 0.01-0.55) to have ever had a Pap
test.
Conclusion
Almost half of the population we studied will have difficulty interpreting
written medical materials, even in Spanish. When developing efforts to reach
women who have not been screened, programs and service providers need to be
aware that the women most in need of information about screening may be more
likely to be unable to read any written materials provided to them, regardless
of the language or level of simplicity of the materials. Programs and strategies
need to be implemented to increase screening prevalence and to minimize the
identified gaps in regular screening for Latinas who have low health literacy.
Back to top
Introduction
Health literacy has been defined as “the degree to which individuals have the
capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and
services needed to make appropriate health decisions” (1). Improving health
literacy has been added as a Healthy People 2010 objective (2), and two recent
reports by the Institute of Medicine and the Agency for Healthcare
Research and Quality summarize the data regarding the prevalence of low
health literacy and its relationship to health care quality, use, outcomes, and
disparities (3,4). Despite these findings, health care providers are
often unaware of the health literacy skills of their patients (5–7).
While there has not been a large-scale study representative of the U.S.
population examining health literacy per se, the 1992 National Adult
Literacy Survey indicated that 40–44 million Americans demonstrated skills in
the lowest level of literacy proficiency in three scales (prose, document, and
quantitative) (8). Some populations are more likely to have lower
literacy skills, including the elderly, non-native English speakers, those with
limited formal education, immigrants, and those with low incomes (8-11).
In New York City alone, according to the 2000 U.S. Census, more than 1.22
million foreign-born residents arrived in the United States in the previous 10
years (12).
There are numerous barriers to effective cervical cancer screening,
particularly for populations with low health literacy: screening recommendations
for cervical cancer are complex (13,14), and educational materials
are often written at reading levels that are inappropriately high for most of
the population (15,16). For women who are native Spanish speakers,
there are even fewer appropriate materials. Cervical cancer is preventable and
treatable if detected early, yet in 2004 there will be an estimated 10,520 new
cases of invasive cervical cancer diagnosed in the United States, and 3900
cervical cancer deaths (17). Case-control studies have found that the risk of developing
invasive cervical cancer is three to 10 times greater in women who have not been
screened (18). SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) data show that
cervical cancer incidence among Latinas aged 30 years and older is almost two
times higher than the rate among non-Hispanic white women (19), which
likely reflects disparities in screening prevalence (20-22). Low
income, educational attainment, acculturation, and literacy may contribute to
lower rates of screening (20,23-25).
As the populations at risk for low health literacy continue to increase both
in New York City and in the United States, and the ethnic disparities in
cervical cancer incidence widen, reducing the health-literacy–related barriers
to cervical cancer screening and appropriate follow-up becomes an even more
serious public health concern. Building on a previously published study that
found an association between health literacy (in English) and Papanicolaou (Pap)
test knowledge among a multiethnic group of young women (7), our
study examined the independent association between functional health literacy in Spanish among low-income Latinas aged 40 and older and cervical cancer
screening knowledge and behavior.
Back to top
Methods
Women aged 40 and older were recruited for the study through their younger
female relatives. On approximately three recruitment days each week, from
November 2002 to July 2003, all women who were awaiting appointments for
prenatal care and family planning services at two MIC-Women’s Health Services
Centers operated by Medical and Health Research Association of New York City,
Inc (MHRA) were approached in the waiting room. In 2003, the two clinic
recruitment sites had 1879 visits from new prenatal and family planning
patients. For women who self-identified as Latina or Hispanic, were aged 18 or
older, and who had a female relative aged 40 or older living in the New York
City area, the interviewer described the study, provided a flyer, and asked for
the client’s written informed consent to be contacted later to obtain the names
and contact information of relatives aged 40 and older. A total of 1205 young women were approached in the
centers: 936 did not fit the above listed eligibility criteria for referring
participants, 27 were eligible but refused to refer participants, and 242 agreed
to refer a participant. Older relatives were eligible to participate in the
study if they self-identified as Latina or Hispanic, were aged 40 or over, and
spoke Spanish as their primary language. Of the 242 women contacted for the study, 25 (10%) refused participation and
seven (3%) were
ineligible (two spoke English as a first language, five were under age 40). A
total of 210 Latina women of various nationalities, ranging in age from 40–78,
consented to participate in the study. Five
participants completed the survey but refused participation in the Test of
Functional Health Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA-S), a screening instrument in
Spanish that has been used in several settings to identify patients with low
functional health literacy; these women were not included in the analysis,
leaving a final sample size of 205. The study was approved by MHRA’s
Institutional Review Board.
The interviews were administered in Spanish in participants’ homes by a
trained and experienced bilingual interviewer. Participation in the study
included written informed consent, administration in Spanish of a 20-minute survey
on cervical cancer screening knowledge and behavior, administration of
the Spanish version of the TOFHLA-S and, for a randomly selected subset of 10%
of participants, medical record release for validation of the most recent Pap
test. All materials, including the consent form and survey, were written in
Spanish and were read aloud to all participants. Materials were developed using
simple words and short sentences. The informed consent (158 words) had an
average of 14 words per sentence and average of 2.1 syllables per word. The
survey, which included 36 questions, had an average of 10 words per sentence and
1.9 syllables per word. To facilitate recall and to reduce inconsistencies in
reporting, the survey was developed using cognitive interviewing techniques in
which participants were asked to verbalize their thought processes as they
completed the survey (26). The survey was developed for the purposes of this
study; several of the survey questions were adapted from a previous study on
breast cancer screening knowledge and behavior (27). The survey was developed in
English, translated to Spanish, and back-translated for review. Survey items
included demographic information, most recent visits to health care providers,
and detailed information on the most recent Pap test, from appointment making
through follow-up. Open-ended questions asked about the purpose of a Pap test,
how a Pap test is performed, and knowledge of risk factors for cervical cancer.
The survey asked participants about the Pap test provider (type of site where
the participant had her last Pap test [e.g., hospital, clinic, private physician
office] and nation of provider [United States or native country]). Follow-up
measures included whether the participant received her results, how she got
results (e.g., postcard, phone call, visit to the provider), whether she was
asked to return for a repeat Pap test, and whether she obtained her last two Pap
tests in the same place.
Participants completed the TOFHLA-S. The English version of the TOFHLA has
been tested for concurrent validity with other standardized literacy tests
(28,29), but because there are no Spanish versions of the other
standardized tests (REALM and WRAT-R) (30), concurrent validity with TOFHLA-S has
not been measured. The TOFHLA-S includes both reading comprehension (employing a
modified Cloze procedure) and numeracy sections. The results of the test yield a
score from 0–100 that includes equal contributions from each section. The test
takes up to 22 minutes to administer. The TOFHLA-S score is categorized into
three levels: those with inadequate functional health literacy (TOFHLA score
0–59) are unable to read and interpret health texts, those with marginal
functional health literacy (TOFHLA score 60–74) have difficulty reading and
interpreting health texts, and those with adequate functional health literacy
(TOFHLA score 75–100) can read and interpret most health texts.
Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistical software version 9.0 (SPSS,
Inc, Chicago, Ill). Statistical differences in the frequencies of demographic
characteristics, health care access (three dimensions: having any health
insurance, having a regular source of care, and visiting any provider in the
last 12 months), and Pap test knowledge, behavior, and follow-up by functional
health literacy groups were assessed by chi-square tests for categorical
variables and analysis of variance for continuous variables. Bivariate odds
ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated for functional health
literacy and demographic variables and Pap test behaviors. Using logistic
regression, adjusted odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated
for ever having a Pap test and having one in the last three years as the dependent
variables, adjusting for characteristics associated with screening behavior (having a source of care
[no {ref}/yes], having any health insurance [no
{ref}/yes], age [40–49 {ref}, 50-59, 60 or older]) and those known to be
associated with literacy (8) (years in the United States [0–14 years {ref}, 15
or more years {dichotomized at the median value}], education [elementary or less
{ref}, some high school or more], and TOFHLA-S score [adequate {ref}, marginal,
inadequate]) (31). A second logistic regression model separated women
with inadequate functional health literacy into two groups: those who scored 1
or above, and those who scored 0 (unable to read any words).
Back to top
Results
Table 1 presents sociodemographic and health information for
the 205 women in the
sample. More than half the women had elementary school education or less, and
95% were foreign-born. Access to care was low, according to three measures
studied: 58% had no health insurance, 41% had no regular source of health care,
and 22% had not visited any doctor in the last year. Almost all of the women
interviewed had heard of a Pap test, and 92% had ever had a Pap test. While 75%
could identify (in an open-ended question) that the purpose of a Pap test was to
detect cancer, only three women specified cervical cancer. As illustrated in
Figure 1, scores on the TOFHLA-S indicated a population with low health literacy
levels in Spanish: 30% had inadequate health literacy in Spanish, 19% marginal,
and 51% adequate. Twenty-four women (12%) were unable to read any words (TOFHLA-S
score of 0). Significant differences were found by functional health literacy
level on sociodemographic variables (except birthplace), knowledge of cervical
cancer, and cervical cancer screening behavior. No differences were found in
terms of access to health care: those with adequate health literacy were no more
likely to have health insurance, a regular source of care, or to have visited
any health care provider in the last year.
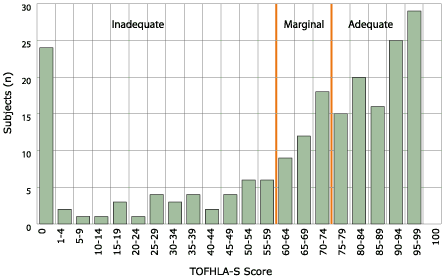
Figure 1. Distribution of scores in functional health literacy as determined by Spanish version of Test of Functional
Health Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA-S) among Latinas aged 40 and older in New York
City, November 2002–July 2003 (N = 205).
Although more than three quarters of the women had had a Pap test in the last
three years, this population faced significant barriers to effective cervical
cancer screening and follow-up, regardless of literacy level: more than 14% did
not receive the results from their most recent Pap test, 10% could not remember where
they had their last Pap test, 29% did not have their last two Pap tests in the same
place, and 26% had their last Pap test in their native country. Figure 2 illustrates
the location of most recent Pap test by literacy level. Compared to those with
adequate and marginal health literacy, women with inadequate health literacy
were significantly less likely to have ever had a Pap test (odds ratio [OR],
0.12; 95% CI, 0.04-0.37) or in the last three years (OR, 0.35; 95% CI,
0.18-0.68), and were significantly more likely to have their last Pap test at a
local public hospital (OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.18-4.97; excluding those who had
never had a Pap test or who could not remember where they had their last Pap
test).
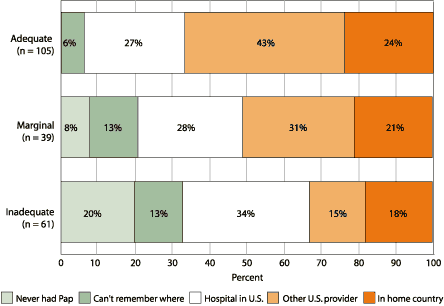
Figure 2. Location of most recent Papanicolaou (Pap) test by functional health literacy level:
survey results among Latinas aged 40 and older in New York City, November 2002–July
2003.
Literacy levels determined by Spanish version of Test of Functional
Health Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA-S).
The goal of the study was to evaluate an independent association of
functional health literacy in Spanish on Pap test behavior, taking into account
factors known to be associated both with lower prevalence of screening and lower
levels of literacy. Table 2 illustrates both the crude and adjusted odds ratios
for ever having a Pap test and having one within the last three years. After adjusting for
source of care, health insurance status, age, years in the United States, and
education, women with inadequate functional health literacy in Spanish (compared
to women with adequate health literacy) were 16.7 times less likely to have ever
had a Pap test (adjusted OR, 0.06; 95% CI, 0.01-0.55). In the adjusted model,
only having a source of health care was found to predict having a Pap test in
the last three years (Adjusted OR, 3.67; 95% CI, 1.45-9.27).
Women who were unable to read any words (comprising 12% of the sample, and
39% of those with inadequate health literacy) were significantly different from
women who had inadequate health literacy as measured by the TOFHLA-S but were
able to read (data not shown in table). Compared to the rest of the sample,
women who were unable to read any words were more recently arrived in the United
States (75% in the United States less than 15 years, compared with 47%,
chi-square = 6.54, P = .009), were significantly older (mean age 61.1
versus 49.6, ANOVA F = 38.96, P < .001), and had fewer years of schooling
(95.8% with elementary education or less, compared to 44.2%, chi-square = 22.99,
P < .001). A second logistic regression (data not shown in table) was
conducted in which health literacy was divided into four strata; women who had
inadequate health literacy but scored higher than 1 on the TOFHLA-S were
categorized separately from those who scored 0 (were unable to read any words),
although this is not a distinction that is made by the developers of the TOFHLA.
In this analysis (with women with adequate health literacy as the referent
group), after adjustment for the same variables as above, women who could not
read any words were four times less likely (adjusted OR, 0.24; 95% CI,
0.07-0.85) to have had a recent Pap test, but no difference was found for women
who had inadequate health literacy but scored higher than 1 on the TOFHLA-S.
Back to top
Discussion
Previous studies of literacy and functional health literacy in the United
States have focused on populations’ abilities to negotiate written information in
English. As Latino populations in the United States continue to grow, exchanges
of health care information will increasingly be provided in Spanish: the 2000 U.S. Census
revealed that 28.1 million Americans speak Spanish, with only half reporting
that they fluently speak English. However, our study suggests that taking the
next step in addressing a health information gap — making materials available in
Spanish — may not be adequate. Almost half of the women we studied will have
difficulty interpreting written medical materials, even if the materials are
made available in Spanish.
Because of low access to care in addition to low levels of functional health
literacy, the study population faces significant barriers in obtaining effective
cervical cancer screening. Our study adds to previous findings by Lindau et al,
in which literacy (in English) was the only factor independently associated with
knowledge of cervical cancer screening, even when controlling for age,
education, ethnicity, employment, and insurance (7). In our study, low levels
of functional health literacy in Spanish were strongly inversely associated with
ever having a Pap test. Even when controlling for other factors (including age,
educational level, having a source of care, having health insurance, and years
in the United States) women with inadequate functional health literacy in
Spanish were 16.7 times less likely to have ever had a Pap test.
Cervical cancer
is preventable and curable if detected early. While the proportion of women we
studied who had ever had a Pap test was high (92%), it is lower than the Healthy
People 2010 objective of 97% (2). Appropriate, regular screening and follow-up
are essential to reduce the identified cervical cancer mortality and incidence
gaps between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites (32). For the outcome of clinical
importance — having a recent (in the last three years) Pap test — the logistic
regression revealed no independent association with functional health literacy
level. A second regression model, however, separating women who could not read
any words, revealed a strong association with having a recent Pap test.
The TOFHLA-S, used to measure health literacy in Spanish, does not distinguish between
those who have inadequate health literacy and those who are unable to read any
words. While the questions in the numeracy section are read aloud, the
participant must be able to read both the prompts in the numeracy section and
the reading comprehension section. Women with lower literacy skills may have
been more likely to refuse participation because of the actual or perceived
literacy burden of the study, resulting in a study population that
underrepresents women with inadequate functional health literacy. It should be
stressed that this study measured functional health literacy in Spanish, the
primary language of participants. We did not measure participants’ functional
health literacy in English, which would allow greater comparability with
previous studies that have examined associations between health literacy in
English and health care knowledge and behavior. An unknown proportion of the
women we studied who were found to have adequate functional health literacy in
Spanish would not have adequate functional health literacy in English, the
primary language in which health care services and education are provided in the
United States.
This study had some other limitations. Previous research suggests that the
prevalence of cervical cancer screening may be overreported (33,34).
Self reporting, as our validation efforts confirmed, consistently results in overreporting of the prevalence of Pap testing (35,36). Because of
the small sample size, the study lacked the power to detect significant effects
of some characteristics that may also contribute to cervical cancer screening
behavior, including nationality, years in the United States, and age. This
analysis focused on Latina immigrant women in New York City whose primary
language is Spanish. Caution should be used in applying the findings to other
ethnic populations, to women living in other areas, or to Latinas whose primary
language is English. Finally, the study examined the association between
functional health literacy and cervical cancer knowledge and behaviors; however,
the scope of the study did not include measurement of the complex relationships
between screening knowledge and behavior.
Our findings are of particular importance to health care providers and
screening programs that serve low-income, immigrant Latina communities. In the
communities we studied, women with low functional health literacy were more
likely to obtain their care at local public hospitals. Our study confirmed
previous findings that women with low health literacy were no less likely to
have a regular source of care and to have had a visit to a provider in the last
year (37). Programs and strategies need to be implemented to increase
screening prevalence and to minimize the identified gaps in follow-up for all
patients. Patient/provider exchanges of all kinds (including those relating to
cervical cancer screening) currently rely on the exchange of written
information, including educational brochures, prescriptions, test results, and
referrals for follow-up. Screening programs and service providers, when
developing efforts to reach women who have not been screened for cervical
cancer, need to be aware that the women most in need of information about
screening may be more likely to be unable to read any written materials provided
to them, regardless of the language or simplicity of the materials. Increasing cervical cancer screening rates and improving follow-up among Latinas
with low functional health literacy will require creative solutions to convey
information without relying on written materials. Providers face the added
challenge that individuals with low functional health literacy may also have
difficulties with oral communication with providers (38). The evidence on the
effectiveness of interventions using innovative approaches such as videotapes is
still emerging (4).
Back to top
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the New York Community Trust. The authors also
wish to thank Maria Uribelarrea, former director of MIC-Women’s Health Services; Dulce Alvarez and Sarina Williams, MIC Center
directors; and Luz Piedrahita,
interviewer.
Back to top
Author Information
Corresponding author: Samantha Garbers, MPA, Medical & Health Research
Association of New York City, Inc, 40 Worth St, Suite 720, New York, NY 10013.
Telephone: 212-285-0220 x119. E-mail: sgarbers@mhra.org.
Author affiliations: Mary Ann Chiasson, DrPH, Medical & Health Research
Association of New York City, New York, NY.
Back to top
References
- Selden CR, Zorn M, Ratzan SC, Parker RM, editors.
Health literacy.
Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine; 2000 Feb.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Healthy people 2010 - understanding and improving health. Washington
(DC): U.S. Government Printing Office; 2000 Nov. 76 p.
- Nielsen-Bohlman L, Panzer AM, Kindig DA, editors. Health literacy: a prescription to
end confusion. Washington (DC): National Academies Press; 2004 Apr 8. 368
p.
- Berkman ND, DeWalt DA, Pignone MP, Sheridan SL, Lohr KN, Lux L, et al.
Literacy and health outcomes. Summary, evidence
report/technology assessment number 87.
Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2004 Jan.
- Bass PF, Wilson JF, Griffith CH, Barnett DR.
Residents' ability to
identify patients with poor literacy skills. Acad Med 2002;77:1039-41.
- Parikh NS, Parker RM, Baker DW, Williams MV, Nurss JR.
Shame and
health literacy: the unspoken connection. Patient Educ
Couns 1996; 27:33-9.
- Lindau ST, Tomori C, Lyons T, Langseth L, Bennett CL, Garcia P.
The
association of health literacy with cervical cancer prevention knowledge
and health behaviors in a multiethnic cohort of women. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
2002; 186:938-43.
- Kirsch IS, Jungeblut A, Jenkins L, and Kolstad A.
Adult
literacy in America: a first look at the findings of the National Adult
Literacy Survey. Washington (DC): U.S. Department of Education, Office
of Educational Research and Improvement; 1993.
- Ad Hoc Committee on Health Literacy for the Council on Scientific
Affairs, American Medical Association.
Health literacy:
report on the Council of Scientific Affairs. JAMA 1999; 281(6): 552-7.
- Greenberg E, Macias RF, Rhodes D, Chan T.
English Literacy and
language minorities in the United States. Washington (DC): U.S.
Department of Education, Office of Educational Research and Improvement;
2001. 234 p.
- Potter LS, Garvey DL, Friedland RB. Who suffers from poor health
literacy? Washington (DC): Center for Health Care Strategies; 1997. 2 p.
- U.S. Census Bureau.
United States Census 2000. Washington (DC): U.S.
Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration; 2000.
- Hartmann KE, Hall SA, Nanda K, Boggess JF, Zolnoun D.
Screening for
cervical cancer. Systematic evidence review number 25. Rockville (MD): Agency for
Healthcare Research and Quality. 2002 Jan.
- Sawaya GF, McConnell KJ, Kulasingam SL, Lawson HW, Kerlikowske K,
Melnikow J, et al.
Risk of
cervical cancer associated with extending the interval between cervical
cancer screenings. N Engl J Med 2003; 349(16):1501-9.
- Doak LG, Doak CC, Meade CD.
Strategies to improve cancer education
materials. Oncol Nurs Forum 1996;23(8):1305-12.
- Rudd R, Moeykens B, Colton T. Health and literacy: a review of the
medical and public health literature. In: Comings J, Garner B, Smith C,
editors. Annual review of adult learning and literacy, volume 1. San
Francisco (CA): Jossey-Bass; 1999 Nov. 384 p.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2004 [Internet].
Atlanta (GA): The Society [cited 2004 Apr 20]. Available from: http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/ CAFF_finalPWSecured.pdf*.
- Physician Data Query.
Screening for
cervical cancer [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
[cited 2004 Apr 22]; 2004.
-
Invasive cervical cancer among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women -
United States 1992-1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rpt 2002;51(47);1067-70.
- Suarez L, Pulley L.
Comparing acculturation scales and their
relationship to cancer screening among older Mexican-American women. J Natl Cancer Inst Monog 1995;(18):41-7.
- Harlan LC, Bernstein AB, Kessler LG.
Cervical cancer screening: who is
not screened and why? Am J Public Health 1991 Jul;81(7):885-90.
- Caplan LS, Wells BL, Haynes S.
Breast cancer screening among older
racial/ethnic minorities and whites: barriers to early detection. J Gerontol 1992 Nov;47 Spec No:101-10.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
1999 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System [Internet]. Atlanta
(GA): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services [cited 2000 Oct 30];
1999.
- Harmon MP, Castro FG, Coe K.
Acculturation and cervical cancer:
knowledge, beliefs, and behaviors of Hispanic women. Women Health 1996;24(3):37-57.
- Bennett C, Ferreira MR, Davis TC, Kaplan J, Weinberger M, Kuzel T, et
al.
Relation between literacy,
race, and stage of presentation among low-income patients with prostate
cancer. J Clin Oncol 1998;16(9):3101-4.
- Jobe JB, Mingay D.
Cognitive Research Improves Questionnaires.
Am J Pub Health 1989;79:1053-5.
- Garbers S, Jessop D, Foti H, Uribelarrea M, Chiasson MA.
Barriers
to breast cancer screening for low-income Mexican and Dominican women in
New York City. J Urban Health 2003;80:81-91.
- Davis TC, Michielutte R, Askov EN, Williams MV, Weiss BD.
Practical
assessment of adult literacy in health care. Health Educ Behav 1998;25(5):613-24.
- Parker RM, Baker DW, Williams MV, Nurss JR.
The
test of functional
health literacy in adults: a new instrument for measuring patients'
literacy skills. J Gen Intern Med 1995;10:537-41.
- Nurss JR, Baker DW, Davis TC, Parker RM, Williams MV. Difficulties in
functional health literacy screening in Spanish-speaking adults. Journal
of Reading 1995;38(8):632-7.
- Nurss JR, Parker RM, Williams MV, Baker DW. TOFHLA: Test of Functional
Health Literacy in Adults. Snow Camp (NC): Peppercorn Press; 1995.
- National Cancer Institute.
A snapshot of cervical cancer
[Internet]. Bethesda (MD): The Institute [cited 2004 Apr 19].
- Marcus AC, Crane LA, Kaplan CP, Goodman KJ, Savage E, Gunning J.
Screening for cervical cancer in emergency centers and sexually
transmitted disease clinics. Obstet Gynecol 1990 Mar;75(3 Pt 1):453-5.
- Bowman JA, Sanson-Fisher R, Redman S.
The accuracy of self-reported
Pap smear utilisation. Soc Sci Med 1997;44(7):969-76.
- Paskett ED, Tatum CM, Mack D, Hoen H, Case D, Velez R.
Validation of self-reported breast and cervical cancer screening tests
among low-income minority women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1996
Sep;5(9):721-6.
- Newell S, Girgis A, Sanson-Fisher R, Ireland M.
Accuracy of patients'
recall of Pap and cholesterol screening. Am J Pub Health 2000;90(9):1431-5.
- Baker Dw, Parker RM, Williams MV, Clark WS, Nurss J.
The relationship
of patient reading ability to self-reported health and use of health
services. Am J Public Health 1997;87:1027-30.
- Schillinger D, Bindman A, Wang F, Stewart A, Piette J.
Functional
health literacy and the quality of physician-patient communication among
diabetes patients. Patient Educ Couns 2004;52(3):315-23.
Back to top
Tables
 Table 1. Demographic and Health Care Characteristics by Functional Health Literacy Level in Spanish:
Survey Results Among Latinas Aged 40 and Older (n = 205), New York City, November
2002–July 2003a Table 1. Demographic and Health Care Characteristics by Functional Health Literacy Level in Spanish:
Survey Results Among Latinas Aged 40 and Older (n = 205), New York City, November
2002–July 2003a
| |
|
Health Literacy Level in Spanish as Measured by Test of Functional Health
Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA-S) |
| Characteristic |
All Women
(n = 205),
No. (%) |
Inadequate
(n = 61),
No. (%) |
Marginal
(n = 39),
No. (%) |
Adequate
(n = 105),
No. (%) |
|
Sociodemographicb |
| Age (years, mean) |
51.0 |
55.3 |
51.4 |
48.3 |
| Years in United
States (mean) |
17.9 |
13.8 |
21.0 |
19.1 |
|
Birthplacec |
| United States (not
Puerto Rico) |
11 (5.4) |
0 (0) |
2 (5.1) |
9 (8.7) |
| Mexico |
25 (12.3) |
10 (16.4) |
4 (10.3) |
11 (10.6) |
| South America |
84 (41.2) |
26 (42.6) |
16 (41.0) |
42 (40.4) |
| Dominican Republic |
39 (19.1) |
11 (18.0) |
7 (17.9) |
21 (20.2) |
| Puerto Rico |
28 (13.7) |
7 (11.5) |
9 (23.1) |
12 (11.5) |
| Central America |
12 (5.9) |
4 (6.6) |
1 (2.6) |
7 (6.7) |
| Other |
5 (2.5) |
3 (4.9) |
0 (0) |
2 (1.9) |
|
Level of educationd |
| No formal education |
12 (5.9) |
12 (19.7) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
| Elementary school
only |
91 (44.4) |
39 (63.9) |
22 (56.4) |
30 (28.6) |
| Some high school |
38 (18.5) |
8 (13.1) |
5 (12.8) |
25 (23.8) |
| High school
graduate or more |
64 (31.2) |
2 (3.3) |
12 (30.8) |
50 (47.6) |
|
Marital statuse |
| Married or living
as married |
100 (49.5) |
26 (43.4) |
17 (44.8) |
57 (54.8) |
| Never married |
27 (13.4) |
6 (10.0) |
7 (18.4) |
14 (13.5) |
| Separated/divorced
or widowed |
75 (37.1) |
28 (46.6) |
14 (36.9) |
33 (31.7) |
| Health carec |
|
No source of health care |
83 (40.5) |
27 (44.3) |
14 (36.8) |
42 (40.0) |
|
No visit to health care provider in last year |
45 (22.0) |
16 (26.2) |
4 (10.3) |
25 (23.8) |
|
Insurance coveragec |
| No insurance |
118 (57.8) |
37 (60.7) |
18 (47.4) |
63 (60.0) |
| Medicaid and/or
Medicare |
66 (32.3) |
20 (32.8) |
18 (47.4) |
28 (26.7) |
| Private insurance |
20 (9.8) |
4 (6.6) |
2 (5.3) |
14 (13.3) |
| Knowledge |
| Ever heard of a
pelvic examf |
198 (96.6) |
56 (91.8) |
38 (97.4) |
104 (99.0) |
| Ever heard of a
Pap testd |
193 (94.1) |
50 (82.0) |
38 (97.4) |
105 (100.0) |
| Can describe how
a Pap test is performedd |
162 (79.4) |
35 (57.4) |
31 (81.6) |
96 (91.4) |
| Could specify
that Pap was to detect cancerf |
153 (74.6) |
37 (60.7) |
31 (79.5) |
85 (81.0) |
| Ever heard of a
mammogramc |
154 (75.1) |
47 (77.0) |
29 74.4) |
78 (74.3) |
| Behavior |
| Ever had a
pelvic exame |
193 (94.1) |
53 (86.9) |
36 (92.3) |
104 (99.0) |
| Ever had a Pap
testd |
187 (92.1) |
48 (80.0) |
35 (92.1) |
104 (99.0) |
| Had a Pap test
in the last 3 yearse |
157 (76.6) |
38 (62.3) |
32 (82.1) |
87 (82.9) |
|
aMissing data are excluded from totals.
bP < .05, one-way ANOVA for association between literacy
level and characteristic.
cResults are not significant.
dP < .001, chi-square test of association between literacy
level and characteristic.
eP < .01, chi-square test of association between literacy
level and characteristic.
fP < .05, chi-square test of association between literacy
level and characteristic.
 Table
2. Bivariate and Logistic Regression Models of Having a Papanicolaou (Pap) Test Ever and
Within the Last Three Years:
Survey Results Among Latinas Aged 40 and Older (n = 205), New York City, November
2002–July 2003a Table
2. Bivariate and Logistic Regression Models of Having a Papanicolaou (Pap) Test Ever and
Within the Last Three Years:
Survey Results Among Latinas Aged 40 and Older (n = 205), New York City, November
2002–July 2003a
|
Bivariate |
Adjusted |
|
Had Recent Pap (<3 years) |
Ever Had Pap |
Had Recent Pap (<3 years) |
Ever Had Pap |
| Source of care |
| No source of care |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| Has
source of care |
2.82
(1.46–5.44) |
0.81
(0.29–2.29) |
3.67
(1.45–9.27) |
0.83
(0.19–3.54) |
|
Health insurance status |
| No
insurance |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| Private,
Medicaid and/or Medicare |
1.74
(0.89–3.43) |
0.85
(0.32–2.31) |
0.63
(0.23–1.73) |
0.98
(0.22–4.44) |
| Age
(years) |
| 40–49 |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| 50–59 |
0.52
(0.24–1.10) |
0.77
(0.23–2.55) |
0.46
(0.19–1.13) |
1.38
(0.34–5.55) |
| 60 and
older |
0.44
(0.19–0.99) |
0.56
(0.17–1.86) |
0.41
(0.15–1.07) |
1.34
(0.33–5.42) |
| Years
in United States |
| Less
than 15 |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| 15 or
more |
2.05
(1.06–3.97) |
1.46
(0.53–3.99) |
2.05
(0.94–4.47) |
1.20
(0.36–4.06) |
|
Education |
| Elementary or no schooling |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| Some
high school or more |
1.62
(0.85–3.10) |
5.24
(1.46–18.82) |
1.03
(0.44–2.44) |
3.16
(0.60–16.66) |
|
Health Literacy Level |
| Adequate |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
Ref |
| Marginal |
0.95
(0.36–2.48) |
0.11
(0.01–1.11) |
1.31
(0.44–3.85) |
0.14
(0.01–1.41) |
| Inadequate |
0.34
(0.17–0.71) |
0.04
(0.005–0.30) |
0.53
(0.21–1.35) |
0.06
(0.01–0.55) |
|
aValues represent odds ratios (95% confidence intervals). Ref
indicates referent group.
Back to top
*URLs for nonfederal organizations are provided solely as a
service to our users. URLs do not constitute an endorsement of any organization
by CDC or the federal government, and none should be inferred. CDC is
not responsible for the content of Web pages found at these URLs.
|
|
