CDC Levels of Care Assessment Tool (CDC LOCATe)
If you’re interested in participating in or have questions about CDC LOCATe, e-mail drhinfo@cdc.gov.
Use of CDC LOCATe is free.
Risk-Appropriate Care
Risk-appropriate care is a strategy developed to improve health outcomes for pregnant women and infants. States may develop coordinated regional systems to help ensure that pregnant women and infants at high risk of complications receive care at a birth facility that is best prepared to meet their health needs. For example, pregnant women with severe heart conditions need care at facilities that have a full range of specialists available to help care for complex medical conditions. Infants born before 32 weeks gestation should be cared for at facilities with specialized health care providers and equipment to care for infants who are born too early or who are critically ill.
CDC Levels of Care Assessment Tool
Definitions and monitoring of levels of care vary widely among states. To address this issue, CDC developed the CDC Levels of Care Assessment Tool (LOCATe). This web-based tool helps states and other jurisdictions create standardized assessments of levels of maternal and neonatal care. CDC LOCATe is based on the most recent guidelines and policy statements issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
The LOCATe Process
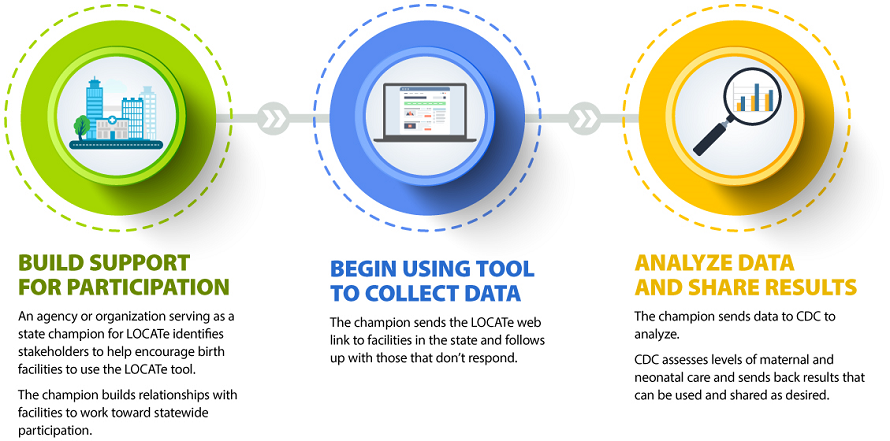
How CDC LOCATe Data Are Used
CDC LOCATe produces standardized assessments that allow participating states to see levels of care by facility, as well as the distribution of staff and services throughout the state. CDC LOCATe data can be combined with public health surveillance data, including vital records and hospital discharge data.
These data allow for more detailed analyses that support understanding of:
- Maternal and infant health outcomes by level of care.
- The relationship between the volume of services provided by a facility and maternal and infant health outcomes.
CDC LOCATe is designed to be used by public health decision makers. This tool can create opportunities for informed conversations among stakeholders who work in the area of risk-appropriate care. Examples of these stakeholders include state and local public health departments, state perinatal quality collaboratives (PQCs), hospital associations, and health care providers working in maternal and neonatal care. The results from CDC LOCATe are a starting point for discussions about how states can improve health outcomes for women and infants.
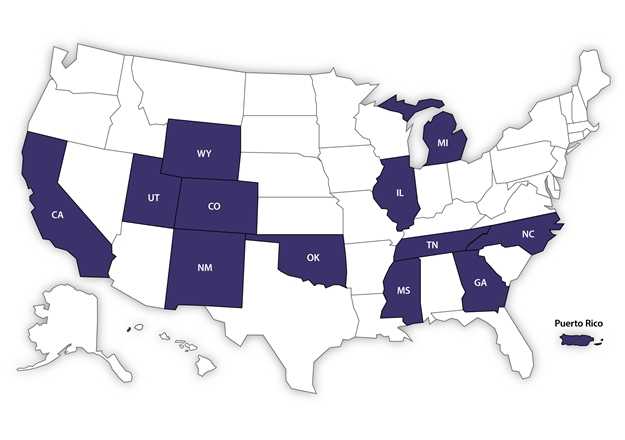
Participating States
As of August 2017, a total of 12 states (California, Colorado, Georgia, Illinois, Michigan, Mississippi, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Utah, and Wyoming) and Puerto Rico are participating in CDC LOCATe.
Related Links
- Levels of Neonatal Care from the American Academy of Pediatrics
- Levels of Maternal Care from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine
- LoMC Levels of Maternal Care from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
- Page last reviewed: August 21, 2017
- Page last updated: August 21, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir