Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP)
GISP Annual Reports and Profiles
- 2015 GISP Profiles (site-specific GISP data)
- 2015 STD Surveillance Report – Gonorrhea (overall GISP data)
- GISP Profiles and Annual Reports All Years
Antibiotic resistance (AR) is the ability of bacteria to resist the effects of all of the drugs used to treat them. This means the germs are not killed and they will continue to reproduce. Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacterium that causes the sexually-transmitted disease gonorrhea, has developed resistance to nearly all of the antibiotics used for gonorrhea treatment.
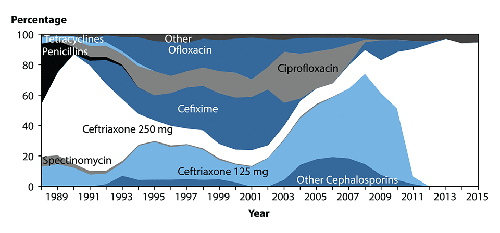
The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) was established in 1986 to monitor AR trends in N. gonorrhoeae bacteria in the United States. GISP is a collaborative project among selected STD clinics and their state or local public health authorities, GISP regional laboratories, and CDC. Public health officials and healthcare providers use the data collected in GISP to ensure that gonorrhea is successfully treated with the right antibiotic.
In GISP, N. gonorrhoeae specimens are collected each month from the first 25 men who attend STD clinics in selected U.S. cities and who have also been diagnosed with urethral gonorrhea. Participating regional laboratories test the specimens for resistance to the antibiotic drugs azithromycin, cefixime, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, penicillin, and tetracycline. These are antibiotics which either are currently or were previously used for gonorrhea treatment. The ability of the bacteria to resist the effect of the antibiotics in the laboratory is measured, and the results are interpreted according to criteria recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). The results of these tests are then transmitted to CDC where they are collated and analyzed.
Recently Published GISP Studies
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae Antimicrobial Susceptibility Surveillance – The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project, 27 Sites, United States, 2014 MMWR July 14, 2016
- Ciprofloxacin resistance and gonorrhea incidence rates in 17 cities, United States, 1991–2006. Emerg Infect Dis [Internet]. 2014 Apr
- Trends in antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States—the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP), January 2006–June 2012. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2013; 89(Suppl 4): iv5–iv10.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae antibiotic resistance among men who have sex with men and men who have sex exclusively with women, the Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project, 2005–2010. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(5):321–328.
- Cephalosporin-resistant gonorrhea in North America. Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 2013;309(2):185–187.
GISP Regional Laboratories and Sentinel Sites
Regional Laboratories
- Emory University, Atlanta, GA
- Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
- Texas Department of State Health Services, Austin, TX
- University of Alabama at Birmingham, AL
- University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Sentinel Sites
- Albuquerque, NM
- Atlanta, GA
- Birmingham, AL
- Boston, MA
- Buffalo, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Cleveland, OH
- Columbus, OH
- Dallas, TX
- Greensboro, NC
- Honolulu, HI
- Indianapolis, IN
- Kansas City, MO
- Las Vegas, NV
- Los Angeles, CA
- Minneapolis, MN
- New Orleans, LA
- New York, NY
- Orange County, CA
- Philadelphia, PA
- Phoenix, AZ
- Pontiac, MI
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Tripler Army Medical center, Honolulu, HI
- Page last reviewed: August 5, 2015
- Page last updated: July 29, 2016
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir