We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Nerve Block: Median
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Useful for lacerations across multiple fingers/palm instead of multiple digit blocks
- Useful for exploration of flexor tendons of digits 1-3
- Ultrasound guidance significantly increases the success rate of this block [1]
Indications
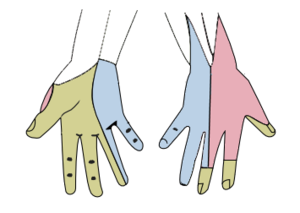
- Trauma or need to perform painful procedure on area innervated by median nerve
Contraindications
- Infection overlying injection site
- Previous allergic reaction to local anesthesic used
- Distortion of anatomic landmarks
Equipment Needed
- Topical anesthesia (LET, EMLA)
- local anesthesia
- Lidocaine 1% (lasts 30-60 minutes or longer if given with epinephrine, rapid onset)
- Mepivacaine 3% (lasts 45-90 minutes, slower onset)
- Bupivacaine 0.5% (lasts 2-4 hours, slowest in onset)
- 18G needle to draw up anesthetic
- 25-30G needle to inject. Use of a larger gauge (21-23) makes it easier to see the needle on ultrasound
- 10 cc syringe
- Gauze pads
Procedure
- Time out, confirm correct patient and laterality
- Apply topical anesthesia if needed
- Draw up 5-10 mL of anesthetic into syringe
- Beware of toxic dose of anesthetic you're using Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity (LAST)
- Before any nerve block, perform neurovascular exam (often includes 2 patient discrimination with paperclip)
Wrist Block
- Median nerve is within the carpal tunnel
- Between palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis
- Insert needle perpendicular between tendons, 2-3 cm proximal to the distal crease of the wrist
- Aspirate; if no blood inject a few mL's of anesthetic slowly
- Test sensation to pain distal to block
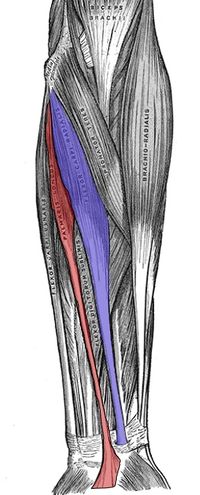
Elbow Block
- Cleanse the skin overlying the antecubital fossa with chosen antiseptic
- Create a sterile field using sterile drape
- In a sterile fashion, apply a small wheel of local anesthetic to the area immediately proximal to the antecubital fossa
- Palpate the brachial artery to be aware of its path
- The median nerve should be approximately 1 cm medial to the brachial artery at this point
- Insert the needle approximately 1-2 cm proximal to the flexor crease and advance with negative pressure applied to the syringe
- At 1-2 cm deep, aspirate prior to injection to rule out intravascular placement
- Inject 5-10 mL of local anesthetic
Ultrasound Guided Block
- Place a linear probe on the volar aspect of the midforearm
- The median nerve takes the appearnce of a "chocolate chip cookie" in the axial orientation and lies between the flexor digitorum profundus and supeficialis
- Clean and prep the patient's arm under sterile conditions, and insert a 25 g needle in the long axis under ultrasound guidance next to the nerve
- Aspirate to prevent inadvertent intravascular injection
- Inject 5 mL of local anesthetic so that it basks the nerve
Complications
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pain
- Needle fracture
- Neurapraxia
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Liebmann O, Price D, et al. [Feasibility of Forearm Ultrasonography-Guided Nerve Blocks of the Radial, Ulnar, and Median Nerves for Hand Procedures in the Emergency Department]. Ann Emerg Med 2006; 48(5):558-62.