We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Intertrochanteric femur fracture
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Occur via fall in elderly or osteoporotic
Clinical Features
- Typically pain, swelling, ecchymosis
- May lose 1-2L of blood
- Unable to bear weight
- Shortening and external rotation if fracture is significantly displaced
Differential Diagnosis
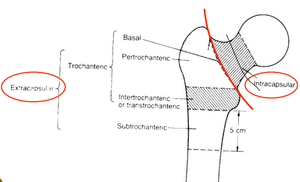
Femur fractures
Proximal
- Intracapsular
- Extracapsular
- Intertrochanteric femur fracture
- Trochanteric femur fracture
Shaft
- Mid-shaft femur fracture (all subtrochanteric)
Evaluation
- Consider AP pelvis in addition to AP/lateral views to compare contralateral side
- Consider MRI if strong clinical suspicion but negative x-ray
Evaluation
- Stable (Garden's type I and II)
- Lesser trochanter non-displaced, no comminution, medial cortices of prox/distal fragments aligned
- Unstable (Garden's type III and IV)
- Displacement occurs, comminution is present, or multiple fracture lines exist
Management
- Admit for eventual ORIF
Disposition
- Admit