We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Molar pregnancy
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Type of gestational trophoblastic disease
- Neoplasm of placental hCG-producing trophoblast cells
- Non-invasive (invasive form is choriocarcinoma, can metastasize to brain, liver, lung)
- Non-viable fertilized egg implants in uterine wall
- Complete: all chorionic villi are vesicular, swollen, with no embryonic development
- Partial: some vesicular chorionic villi, +/- (nonviable) embryonic development
Clinical Features
Due primarily to elevated levels of hCG
- Vaginal bleeding (75-95%)
- Hyperemesis gravidarum (26%]]
- Hypertension, preeclampsia
- Suspect molar pregnancy when pregnancy-induced hypertension occurs at <24 weeks
- Larger than usual uterine size
- Signs/symptoms of hyperthyroidism (rarely)
Differential Diagnosis
- Vaginal bleeding
- Ectopic Pregnancy, heterotopic pregnancy
- First Trimester Abortion (complete, threatened, incomplete, septic, etc.)
- Implantation bleeding
- Fibroids
- Cervicitis
- Gestational trophoblastic disease
Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy
- Hyperemesis gravidarum
- Gastroenteritis
- Biliary disease
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Gastroenteritis
- Pancreatitis
- Appendicitis
- Hepatitis
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Pyelonephritis
- Fatty liver of pregnancy
- HELLP syndrome
- Gestational trophoblastic disease (may present with intractable vomiting)
- Thyrotoxicosis (may present with intractable vomiting)
- Molar pregnancy
Evaluation
- Serum hCG
- Evaluate for other causes of or electrolyte derangements due to vomiting
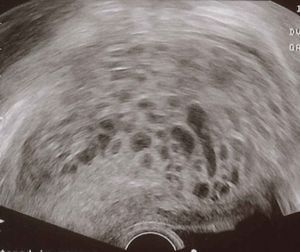
- Ultrasound: enlarged uterus with interspersed lucent and brighter areas ("snowstorm" appearance)
Management
- Ob/gyn consult
- Suction curettage as inpatient (due to risk of bleeding)
- Resuscitate if severe bleeding
- Treat preeclampsia
- Symptomatic resuscitation of nausea/vomiting
Disposition
- Admit