We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Otic barotrauma
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Also known as "ear squeeze" - generally seen during scuba diving or air travel
Clinical Features
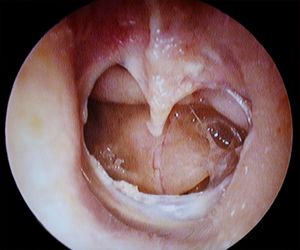
Middle Ear
- Results from inability to equalize middle ear pressure
- Pain, fullness, vertigo, conductive hearing loss, TM rupture
Inner Ear
- Results from forceful valsalva against an occluded eustachian tube
- Pressure difference between middle ear and inner ear can rupture oval or round window
- Sudden onset of sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, severe vertigo
Differential Diagnosis
Scuba Diving Emergencies
- Barotrauma of descent
- Otic barotrauma
- Sinus barotrauma
- Face squeeze
- Barotrauma of ascent
- At depth injuries
- Oxygen toxicity
- Nitrogen narcosis
- Hypothermia
- Contaminated gas mixture (e.g. CO toxicity)
Ear Diagnoses
- External
- Auricular hematoma
- Cholesteatoma
- Contact dermatitis
- Ear foreign body
- Herpes zoster oticus (Ramsay Hunt syndrome)
- Malignant otitis externa
- Mastoiditis
- Otitis externa
- Otomycosis
- Tympanic membrane rupture
- Internal
- Acute otitis media
- Bullous myringitis
- Chronic otitis media
- Mastoiditis
- Otic barotrauma
- Inner/vestibular
Barotrauma Types
- Otic barotrauma
- Pulmonary barotrauma
- Sinus barotrauma
Evaluation
- Generally clinical
Management
Middle Ear
- Decongestants
- Consider antibiotics if typmanic membrane ruptured
Inner Ear
- Elevate head of bed
- Advise patient to not blow nose
- Antivertigo medications
- ENT consult
Disposition
- Generally may be discharged
See Also
External Links
References
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Michael Holtz, Daniel Ostermayer, Neil Young