We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
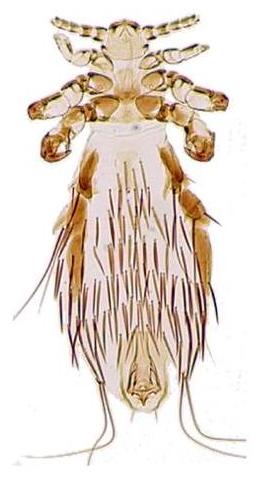
Lice
From WikEM
(Redirected from Pediculosis pubis)
Contents
Background
- Caused by Pediculus humanus
- Hats/combs may act as fomites
Clinical Features
- May see live mites or nits (egg sacks) on hair shaft close to scalp
- May be asymptomatic or pruritic
Differential Diagnosis
Ectoparasites
Evaluation
- Generally a clinical diagnosis
Management
Over the Counter (OTC)
- Permethrin 1% lotion shampoo (if >2 months old)[1]
- Wash hair with non-conditioned shampoo
- Apply Permethrin for 10 min and rinse
- Repeat on day 9
- Pyrethrin lotion
- Apply to affected areas and wash off after 10 min
- Repeat in 7 days
Prescription
Reserved for failed OTC treatment
- Spinosad 0.9% topical suspension (if >6 months old)
- Apply to scalp and air and wash off after 10 min.
- Repeat in 10 days
- Malathion 0.5% lotion (if >6 years old)
- Applied to affected areas and wash after 8 hrs
- Repeat in 7 days
- Benzyl Alcohol 5% lotion (> 6 months old)
- Apply to dry hair and wash off after 10 min
- Repeat in 7 days
- Ivermectin 400mcg/kg PO
- Once on day 1 THEN once in 7 days
- Reserved for patients failing topical treatment
- Lindane therapy
- Only consider if patient has failed two prior prescription treatments
- Avoid in children <50 kg due to seizure association
Eyelash Infestation
- Apply ophthalmic petroleum jelly q12hrs x 10 days
Pediatrics <2yo
- Wet combing is an alternative to medical therapy
Disposition
- Discharge
- Children can return to school after first topical treatment has been applied
- Instruct parents and all close contacts to wash clothing and bedding in hot soapy water to avoid disease spread
See Also
References
- ↑ Devore CD and Schutze G. Head Lice. Pediatrics. 2015; 135(5) e1355-e1365.