We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Radiograph-negative ankle injury (peds)
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Pediatric ankle injuries are common (>2 million ED visits in North America per year)[1]
- Historically, there has been concern about missing a potential growth plate fracture (Salter-Harris Type 1), which can rarely result in growth arrest[1]
- It was previously taught that the weaker physis would fail before the stronger ligamentous complex.[2]
- This was commonly treated with immobilization (casting), follow-up imaging, and orthopedic referral (as opposed to adult ankle sprain)
- Recent studies have questioned the need for this practice[3][4]
- There was no measurable difference in functional recovery for children with or without Salter Harris Type 1 distal fibula fractures at 1 and 3 months[4]
Clinical Features
- Lateral ankle pain (tenderness and/or swelling) after inversion injury in a pediatric patient
- Studies to date have not addressed medial ankle pain
Differential Diagnosis
- Ankle fracture
- Salter-Harris fracture
- Ligimentous injury
- Contusion of bone or soft tissue
Evaluation
- Consider ankle x-rays
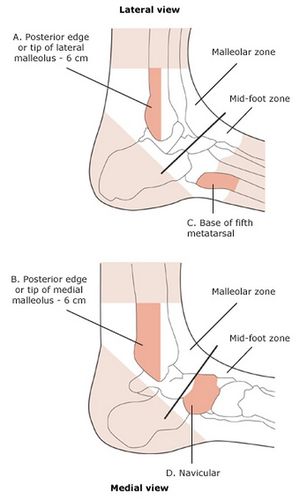
Ottawa ankle rule
Ankle x-ray needed if:
- Pain near the maleoli AND
- Inability to bear weight immediately and in the ED (4 steps) OR
- Tenderness at posterior edge or tip of lateral malleolus OR
- Tenderness at posterior edge or tip of medial malleolus
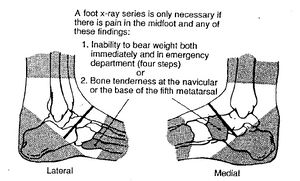
Ottawa foot rules
Foot x-ray series needed if:
- Pain in the midfoot AND
- Inability to bear weight both immediately and in the ED (4 steps) OR
- Tenderness at the navicular OR
- Tenderness at the base of the 5th metatarsal
Management
- Removable ankle brace
- Return to activities as tolerated by pain
Patients do NOT need
- Full immobilization (cast or non-removable splint)
- Referral to orthopedics
- Repeat x-ray films (or MRI)
Disposition
- Discharge with PCP follow-up
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gill PJ, Klassen T. Revisiting radiograph-negative ankle injuries in children: is it a fracture or a sprain? JAMA Pediatr. 2016; 170(1):e154147-e154147.
- ↑ Blackburn EW, Aronsson DD, Rubright JH, Lisle JW. Ankle fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(13):1234-1244.
- ↑ 6. Boutis K, Narayanan UG, Dong FF, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of clinically suspected Salter-Harris I fracture of the distal fibula. Injury. 2010;41(8):852-856.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Boutis K, Plint A, Stimec J, et al. Radiograph-negative lateral ankle injuries in children: occult growth plate fracture or sprain? JAMA Pediatr. 2016; 170(1):e154114-e154114.