We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt overdrainage
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Overdrainage → tissue occluding the orifices of the proximal shunt apparatus
- As pressure increases the occluding tissue diesengages allowing drainage to resume
- Leads to cyclic increased ICP complaints that worsen when patient stands
- Newer valve devices with antisiphon features make this less common
Clinical Features
- Vague symptoms of dizziness, visual distubances
- Worsened with standing/exertion
Differential Diagnosis
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt problems
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt obstruction
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt overdrainage (Slit Ventricle Syndrome)
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt infection
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt mechanical failure
Evaluation
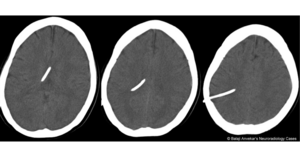
- CT Head necessary for shunt placement workup and overdrained ventricles
- Patients at higher risk for subdural hematomas
Management
- Neurosurgery consult
Disposition
- Admission for shunt revision versus valve adjustment
See Also
External Links
References
Authors
Ross Donaldson, Justin Arndt, Claire, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer, Michael Holtz