Gastrointestinal Anthrax
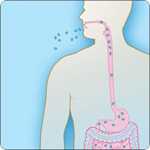 When a person eats raw or undercooked meat from an animal infected with anthrax, they can develop gastrointestinal anthrax. Once ingested, anthrax spores can affect the upper gastrointestinal tract (throat and esophagus), stomach, and intestines.
When a person eats raw or undercooked meat from an animal infected with anthrax, they can develop gastrointestinal anthrax. Once ingested, anthrax spores can affect the upper gastrointestinal tract (throat and esophagus), stomach, and intestines.
Gastrointestinal anthrax has rarely been reported in the United States. Infection usually develops from 1 to 7 days after exposure. Without treatment, more than half of patients with gastrointestinal anthrax die. However, with proper treatment, 60% of patients survive.
Learn More
- Page last reviewed: July 21, 2014
- Page last updated: July 21, 2014
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir