Content on this page was developed during the 2009-2010 H1N1 pandemic and has not been updated.
- The H1N1 virus that caused that pandemic is now a regular human flu virus and continues to circulate seasonally worldwide.
- The English language content on this website is being archived for historic and reference purposes only.
- For current, updated information on seasonal flu, including information about H1N1, see the CDC Seasonal Flu website.
2009 H1N1 Flu: International Situation Update
May 28, 2010, 5:15 PM ET
This report provides an update to the international flu situation using data collected through May 23, 2010, and reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) on May 28.
WHO continues to report laboratory-confirmed 2009 H1N1 flu deaths on its web page. These fatal cases are an under-representation of the actual numbers as many deaths are never tested or recognized as influenza related.
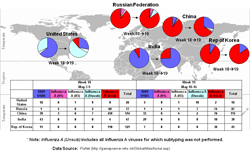
The most active areas of 2009 H1N1 influenza transmission are in the tropical regions of the Caribbean and Southeast Asia. In the tropical regions of South America, 2009 H1N1 and seasonal influenza viruses continue to co-circulate at low levels. Influenza B has been reported at low but increasing levels in certain South American countries.
Influenza activity is low in most parts of the temperate Northern and Southern hemispheres, except for Chile, which has localized areas of 2009 H1N1 influenza activity. Intermittent detections of seasonal influenza A (H3N2) and 2009 H1N1 influenza viruses have been recently reported in Australia. In the European region, influenza activity is low and at levels normally seen during the summer. In addition, a low percentage (4.5%) of respiratory specimens collected in the European region through May 23, 2010, and submitted for laboratory testing have tested positive for influenza. Of the 80 influenza virus detections reported this week, 86% were influenza B. In Sub-Saharan Africa, 2009 H1N1 influenza activity in West Africa has now largely subsided.
Selected Highlights
- • According to WHO, the majority of 2009 H1N1 virus isolates tested worldwide remains sensitive to oseltamivir, an antiviral medicine used to treat flu. Among 2009 H1N1 isolates tested worldwide, 290 have been found to be resistant to oseltamivir – 67 of these isolates were detected in the United States. Approximately 1% of U.S. 2009 H1N1 viruses tested by CDC since September 1, 2009, have been resistant to oseltamivir.
- Influenza B was reported as the predominating influenza virus accounting for 66.1% of all influenza detections in China (Hong Kong SAR), 84.4 % in the Republic of Korea and 85.1% in the Russian Federation.
- Sporadic detections of seasonal influenza A(H1N1) virus were reported in China and the Russian Federation, and influenza A(H3N2) activity has been reported from China, Ghana, Kenya, and Thailand recently.
- On February 18, 2010, WHO published recommendations for the following viruses to be used for influenza vaccines in the 2010-2011 influenza season of the Northern Hemisphere:
- an A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like virus;
- an A/Perth/16/2009 (H3N2)-like virus*;
- a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus.
* A/Wisconsin/15/2009 is an A/Perth/16/2009 (H3N2)-like virus and is a 2010 Southern Hemisphere vaccine virus.
Health Organizations
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control)
- H2P (Humanitarian Pandemic Preparedness)
- Public Health Agency of Canada
World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Offices
- AFRO (WHO Regional Office for Africa)
- AMRO (WHO Regional Office for the Americas) / PAHO (Pan American Health Organization)
- EMRO (WHO Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean)
- EURO (WHO Regional Office for Europe)
- SEARO (WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia)
- WPRO (WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific)
Travel and 2009 H1N1 Flu
Human cases of 2009 H1N1 flu virus infection have been identified in the United States and several countries around the world. For information on 2009 H1N1 flu and travel, see the CDC H1N1 Flu and Travel website.
Reports and Publications
- White House Report on 2009 H1N1 in the Southern Hemisphere
Issued August 2009 – This White House report was prepared by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) in coordination with the Office of the Director for National Intelligence (ODNI) and the Department of State (Dos) and describes the characteristics and impact of 2009 H1N1 influenza A virus in the Southern Hemisphere. - ECDC Interim Risk Assessment Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Pandemic
Issued July 30, 2009 - This document provides an interim risk assessment of novel H1N1 flu in Europe prepared by ECDC. - World Health Organization Weekly Epidemiological record – Issued July 24, 2009
This document by WHO provides updates on the international novel H1N1 flu situation. - MMWR – Update: Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection – Mexico, March-May, 2009 – Issued June 5, 2009 / Vol. 58 / No. 21.
This Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report describes the novel influenza A (H1N1) outbreak in Mexico from March-May, 2009. - MMWR – Update: Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infections – Worldwide, May 6, 2009 – Issued May 8, 2009 / Vol. 58 / No. 17.
This Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report describes worldwide novel influenza A (H1N1) infections as of May 6, 2009.
Get email updates
To receive weekly email updates about this site, enter your email address:
Contact Us:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
1600 Clifton Rd
Atlanta, GA 30333 - 800-CDC-INFO
(800-232-4636)
TTY: (888) 232-6348 - Contact CDC-INFO