Assessing Your Weight
A high amount of body fat can lead to weight-related diseases and other health issues and being underweight can also put one at risk for health issues. BMI and waist circumference are two measures that can be used as screening tools to estimate weight status in relation to potential disease risk. However, BMI and waist circumference are not diagnostic tools for disease risks. A trained healthcare provider should perform other health assessments in order to evaluate disease risk and diagnose disease status.
How to Measure and Interpret Weight Status
Adult Body Mass Index or BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person's weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. A high BMI can be an indicator of high body fatness and having a low BMI can be an indicator of having too low body fatness. BMI can be used as a screening tool but is not diagnostic of the body fatness or health of an individual.To calculate your BMI, see the BMI Calculator. Or determine your BMI by finding your height and weight in this BMI Index Chart 1.
- If your BMI is less than 18.5, it falls within the underweight range.
- If your BMI is 18.5 to 24.9, it falls within the normal or Healthy Weight range.
- If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range.
- If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range.
Weight that is higher than what is considered as a healthy weight for a given height is described as overweight or obese. Weight that is lower than what is considered as healthy for a given height is described as underweight.1
At an individual level, BMI can be used as a screening tool but is not diagnostic of the body fatness or health of an individual. A trained healthcare provider should perform appropriate health assessments in order to evaluate an individual's health status and risks.
How to Measure Height and Weight for BMI
Height and weight must be measured in order to calculate BMI. It is most accurate to measure height in meters and weight in kilograms. However, the BMI formula has been adapted for height measured in inches and weight measured in pounds. These measurements can be taken in a healthcare provider’s office, or at home using a tape measure and scale.
For more, see About Adult BMI.
Waist Circumference
How To Measure Your Waist Circumference2
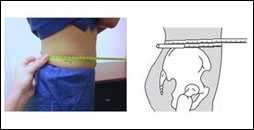
To correctly measure waist circumference:
- Stand and place a tape measure around your middle, just above your hipbones
- Make sure tape is horizontal around the waist
- Keep the tape snug around the waist, but not compressing the skin
- Measure your waist just after you breathe out
Another way to estimate your potential disease risk is to measure your waist circumference. Excessive abdominal fat may be serious because it places you at greater risk for developing obesity-related conditions, such as Type 2 Diabetes, high blood pressure, and coronary artery disease. Your waistline may be telling you that you have a higher risk of developing obesity-related conditions if you are1:
- A man whose waist circumference is more than 40 inches
- A non-pregnant woman whose waist circumference is more than 35 inches
Waist circumference can be used as a screening tool but is not diagnostic of the body fatness or health of an individual. A trained healthcare provider should perform appropriate health assessments in order to evaluate an individual's health status and risks.
Note: The information on these pages is intended for adult men and non-pregnant women only. To assess the weight of children or teenagers, see the Child and Teen BMI Calculator.
Want to learn more?
Preventing Weight Gain
Choosing a lifestyle that includes good eating habits and daily physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight and prevent weight gain.
The Possible Health Effects from Having Obesity
Having obesity can increase your chances of developing certain diseases and health conditions.
Losing Weight
If you are overweight or have obesity and have decided to lose weight, even modest weight loss can mean big health benefits.
Underweight
If you are concerned about being underweight, please seek a trained healthcare provider. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Healthy Weight Gain webpage provides some information and advice on how to gain weight and remain healthy.
References
1NBHLI. The Practical Guide for Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults [PDF -1.51MB]. 2000.
2DHHS. A Healthier You. 2005.
- Page last reviewed: May 15, 2015
- Page last updated: May 15, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
