Other Presentations of Hansen’s Disease
Various presentations and complications of the disease involving the nerves, eye, facial structures, and hands and feet in advanced Hansen’s disease are shown below.
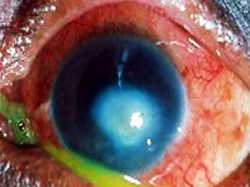
Staphyloma (MB Hansens’s disease)
This patient presented in a clinical setting with a case of multibacillary leprosy. The photo shows one of the complications of this disease: staphyloma of the left eyeball. A staphyloma involves the protrusion of the wall of the eyeball, exhibiting a dark coloration due to the fact that the inner wall of the globe is pigmented and pushed towards its surface. This degeneration to the globe is a direct result of this illness.
Nose skin changes (MB Hansens’s disease)
From a left lateral perspective, the nose of this patient exhibited cutaneous changes that after a complete differential diagnostic study proved to be multibacillary leprosy. The skin surface had been transformed into reddish-brown nodules atop the left ala, and it appears that the disease process included the left nare and nasal vestibule. Ruled out in the diagnosis was scleroma, syphilis, and malignancy in general.
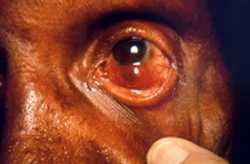
Saddle-nose deformity
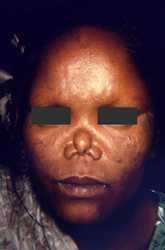
The face of this female patient exhibited some of the complications associated with multibacillary leprosy. Of note was the depressed nasal bridge known as saddle-nose deformity due to the disintegration of the nasal cartilage in this area. Also note the lack of eyebrows and the mottled coloration of the sclerae bilaterally.
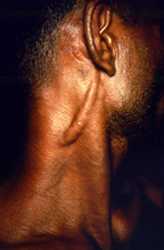
Ear lesion (PB Hansen’s disease)
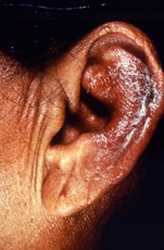
This patient presented to a clinical setting with an inflammatory lesion on the outer left ear, or pinna, which having undergone a differential diagnosis, was determined to be the paucibacillary form of Hansen’s disease. Eliminated as possible pathologic processes were lupus vulgaris and eczematous dermatitis.
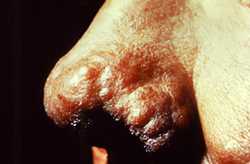
Hands digit erosion (MB Hansen’s disease)
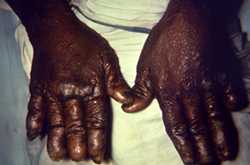
This image depicts the dorsal surface of the hands of a patient with a case of nodular multibacillary leprosy. The digits of both hands had been eroded over the course of the illness, and the skin exhibited numerous cutaneous nodules, which were indicative of late-stage disease.
Resorption of digits on hand (MB Hansen’s disease)
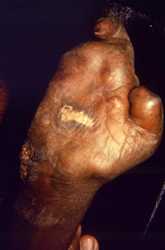
This image depicts the ventral surface of the right hand of a patient with a case of multibacillary leprosy. At this late stage, the digits have been almost fully resorbed, except for the index finger, and the proximal remnant of the thumb. There is also a granulomatous inflammatory lesion located on the palmar surface.
- Page last reviewed: January 31, 2017
- Page last updated: January 31, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir