Reactive Episodes
At least one in four patients with Hansen’s disease experience reactive episodes – or “reactions” – during their treatment, although reactions may occur before treatment begins or after it is completed. Reactions are not due to medications used to treat the disease, although people treated with clofazimine tend to have slightly fewer episodes. There are two main groups of reactions:
- Type 1 reactions, also called reversal reactions, are typical in PB or tuberculoid Hansen’s disease, and also in its borderline presentations, and show up as edema and erythema of pre-existing lesions. In some cases, neuritis and rarely new lesions or fever may also occur.
- Type 2 reactions or Erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) are most frequently seen in patients with MB or lepromatous Hansen’s disease. Patients usually present with painful erythematous nodules, often distributed between existing lesions, and moderate to high fever. Inflammation of other tissues may be present, including peripheral neuritis, orchitis, lymphadenitis, iridocyclitis, nephritis, periostitis and arthralgias.
- Lucio’s phenomenon, a rare reaction characterized by multiple hard-to-heal ulcers of varying size, is usually seen in patients with diffuse lepromatous leprosy who are of Mexican ancestry.
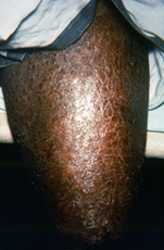
The photo shows the left thigh of a patient who had presented to a clinical setting with a case of multibacillary leprosy. One of its symptoms exhibited here is known as erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL). Note the numerous red-purple papules, nodules and plaques that comprise these lesions. A possible cause for this pathologic manifestation is the overabundance of antibody production leading to the deposition of immune complexes in the affected tissues, which triggers this immunologically-based inflammatory response. Usually these maculopapular plaques crop up between already-existing lepromatous lesions.
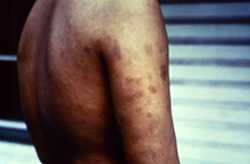
Viewed from a right posterolateral perspective, this patient had presented to a clinical setting with a case of multibacillary leprosy, and one of its symptoms shown here is erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL). Note the numerous cutaneous erythematous blotchy lesions on the patient’s back, right shoulder, and upper arm.
- Page last reviewed: February 10, 2017
- Page last updated: February 10, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir