 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail. Disparities in Deaths from Stroke Among Persons Aged <75 Years --- United States, 2002Despite declines in deaths from stroke, stroke remained the third leading cause of death in the United States in 2002,
and age-adjusted death rates for stroke remained higher among blacks than whites
(1). In 1997, excess deaths from stroke
occurred among persons aged <65 years in most racial/ethnic minority groups, compared with whites
(2). A younger age distribution among Hispanics and other racial/ethnic groups compared with whites might partly explain the disproportionate burden in deaths at younger ages. To examine disparities in stroke mortality among persons aged <75 years, CDC assessed
several characteristics of mortality at younger ages by using death certificate data for 2002. This report summarizes the results of
that assessment. Overall, 11.9% of all stroke deaths in 2002 occurred among persons aged <65 years; the proportion of
stroke decedents who were aged <65 years was higher among blacks, American Indians/Alaska Natives, and Asians/Pacific Islanders, compared with whites. In addition, the mean ages of stroke decedents were statistically significantly lower in these racial groups than among whites. Blacks had more than twice the age-specific death rates from stroke than whites aged <75 years. Approximately 3,400 excess stroke deaths would not have occurred among blacks in 2002 if blacks had had the same
death
rates for stroke as whites aged <65 years. Moreover, age-adjusted estimates of years of potential life lost (YPLL) before age 75 years from stroke were more than twice as high for blacks than for all other racial groups. Reducing premature death
from stroke in these groups will require early prevention, detection, treatment, and control of risk factors for stroke in young and middle-aged adults. National and state mortality statistics used in this assessment were based on information from death certificates from all
50 states and the District of Columbia (DC). Demographic data (e.g., race/ethnicity, sex, and age) on death certificates were provided by funeral directors or family members. Stroke-related deaths were defined as those for which the underlying causes reported on the death certificate by a physician, medical examiner, or coroner were classified according to International Classification of Diseases, Tenth
Revision (ICD--10) codes I60--I69. Age-specific excess deaths for racial groups were
calculated by subtracting the expected number of deaths (i.e., the population number in a racial group multiplied by the death rate
of whites) from the observed number of deaths within each age-specific group
(2). YPLL before age 75 years was calculated as
the sum of the differences between age 75 years and the midpoint of each of eight age groups <75 years
(3). Age-adjusted estimates for YPLL before age 75 years (per 100,000 persons aged <75 years) in 2002 were calculated by using the 2000 U.S. standard population (3). The mean age at death for all stroke decedents was also calculated.
Age-adjusted death rates (per 100,000 population) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated by using the 2000 U.S. standard population (1). Among U.S. residents, 162,672 stroke deaths occurred in 2002, with an age-adjusted death rate of 56.2 per
100,000 population (Table 1). Age-adjusted rates were higher among blacks (76.3) than whites (54.2) (p<0.05). The overall mean
age of a stroke decedent was 79.6 years; however, males had a younger mean age at stroke death than females (p<0.05).
Blacks, American Indians/Alaska Natives, and Asians/Pacific Islanders had younger mean ages than whites (p<0.05), and the mean
age at stroke death was also younger among Hispanics than among non-Hispanics (p<0.05). Of all stroke deaths in 2002, a total of 19,376 (11.9%) occurred among persons aged <65 years. The proportion of stroke decedents aged <65 was higher among men than women, higher in other racial groups than among whites, and higher among Hispanics than among
non-Hispanics. Overall, 568,575 YPLL occurred before age 75 years from stroke in 2002; this number resulted in an age-adjusted estimate of 208.5 per 100,000 population aged <75 years. Higher age-adjusted estimates of YPLL were observed in males
(227.9) compared with females (190.7) and were more than doubled in blacks (475.3)
compared with whites (173.7) (Table 1). Compared with whites, age-specific death rates for blacks were 2.5 times, 3.5 times, 2.8 times, and 1.9 times
higher (p<0.05) at ages 0--44, 45--54, 55--64, and 65--74 years,
respectively (Figure). This resulted in 3,453.9 excess stroke
deaths among blacks at age <65 years (606.5 at age 0--44 years, 1,352.5 at age 45--54 years, and 1,494.9 at age 55--64 years). Age-specific death rates among American Indians/Alaskan Natives and Asians/Pacific Islanders were slightly higher than
among whites (p<0.05 for age 55--64 years only). Compared with non-Hispanics, Hispanics had lower or similar
age-specific death rates for stroke (CDC, unpublished data,
2005). Age-adjusted death rates, mean age at stroke death, and the proportion of stroke deaths that occurred at age <65 years varied among states and DC (Table 2). In 2002, the age-adjusted death rate for stroke ranged from 37.4 per 100,000 population in New York to 74.3 in Arkansas. The mean age of stroke decedents ranged from 75.5 years in Alaska to 83.4 years in North Dakota. The proportion of stroke deaths occurring at age <65 years ranged from 6.3% in Iowa to 18.2% in Louisiana and 18.3% in DC. Age-adjusted estimates of YPLL from stroke before age 75 years (per 100,000 population aged <75 years) ranged from 132.7 in Vermont to 361.0 in Mississippi in 2002. Reported by: C Harris, MPH, C Ayala, PhD, S Dai, MD, JB Croft, PhD, Div of Adult and Community Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, CDC. Editorial Note:The findings in this report demonstrate racial and ethnic disparities in stroke mortality at age <75 years. In 2002, the mean age of stroke decedents was 79.6 years, and only 11.9% of all stroke deaths occurred among persons aged <65 years. However, considerable differences by race/ethnicity and by area of residence occurred in the proportion of deaths at age <65 years and by race/ethnicity in age-specific mortality rates, excess deaths, and YPLL before age 75 years. Whereas a younger age distribution among Hispanics and other racial groups compared with whites might explain some of the higher proportions of deaths at age <65 years, stroke decedents in these groups die at a younger age than non-Hispanics and whites. Stroke death at younger ages contributes to 8% of the lower life expectancy in blacks compared with whites after accounting for heart disease (27.4%), cancer (19.4%), and homicide (9.7%) (4). Racial and ethnic disparities might also be explained by differences in stroke risk factors among population subgroups and younger adults. For example, among adults aged 45--54 years, during 1998--2002, a statistically higher prevalence of self-reported diabetes was observed for Hispanics than non-Hispanic whites in several states with the highest proportions of Hispanics (5). Hispanics and non-Hispanic blacks also have a higher prevalence of overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity than non-Hispanics whites (3,6), whereas self-reported high blood pressure is higher in blacks than whites (3,6). In certain communities, the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and obesity among American Indians and blacks is considerably higher than in the general population (7). Cigarette smoking tends to be more common in American Indian communities than in other racial or ethnic communities (7). To eliminate these disparities in stroke mortality among persons aged <75 years, public health strategies should focus on detecting and reducing stroke risk factors and improving access to health-care and preventive-care services among young and middle-aged adults in racial and ethnic subgroups at high risk. Variations among states might reflect differences in lifestyle and stroke risk factors
(6). States with the highest proportion of stroke deaths occurring at age <65 years are in the southern region of the United States, which includes a higher percentage of adults with stroke risk factors, such as hypertension, smoking, obesity, and physical inactivity
(6). The disproportionate number of stroke deaths among persons aged <65 years in Alaska, Nevada, and New Mexico might reflect the demographics
of those states, which have greater proportions of American Indian/Alaska Native communities and a high
prevalence of stroke risk factors. The findings in this report are subject to at least two limitations. First, death certificate data are subject to error in
the certification of underlying causes of death
(1). Second, underreporting of American Indian/Alaska Native,
Asian/Pacific Islander, and Hispanic origin on death certificates might lead to underestimates of the proportion of stroke
deaths among persons aged <65 years among these populations
(1,8). Premature death is only part of the health impact of strokes in young and middle-aged adults. An estimated
942,000 hospitalizations for stroke occurred in 2002; of these, 28%
occurred among patients aged <65 years
(9). Approximately 2.3% of whites and 2.7% of blacks living in U.S. households in 2000--2001 reported a history of stroke; approximately half of
black stroke survivors and one third of white stroke survivors were aged <65 years
(10). Black stroke survivors experienced
more limitations of activities than white survivors
(10). The elimination of stroke risk is crucial for reducing not only death but
also stroke disability, thereby improving both the quality of life and life expectancy. Campaigns that increase awareness of
stroke warning signs and symptoms should be continued, particularly among young adults who might perceive stroke as a
health condition limited to the aging
population. References
Table 1  Return to top. Table 2  Return to top. Figure 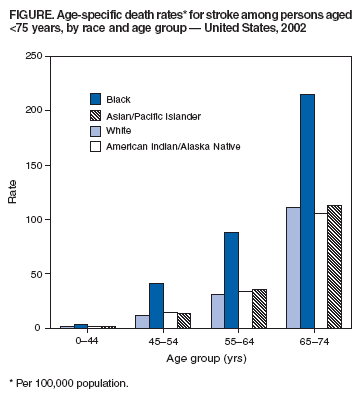 Return to top.
Disclaimer All MMWR HTML versions of articles are electronic conversions from ASCII text into HTML. This conversion may have resulted in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users should not rely on this HTML document, but are referred to the electronic PDF version and/or the original MMWR paper copy for the official text, figures, and tables. An original paper copy of this issue can be obtained from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO), Washington, DC 20402-9371; telephone: (202) 512-1800. Contact GPO for current prices. **Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.Date last reviewed: 5/18/2005 |
|||||||||
|