QuickStats: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease Death Rates* Among Women Aged 45–64 Years, by Race and Age Group — National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2000–2015
Weekly / September 22, 2017 / 66(37);1004
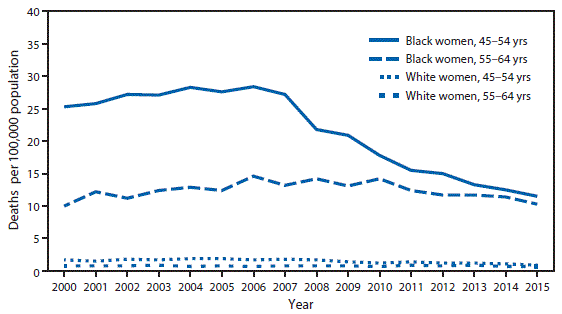
* Deaths include those with underlying cause coded as B20–B24 in the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision.
Among black women aged 45–54 years, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease death rate decreased 60% from 28.4 per 100,000 in 2006 to 11.5 in 2015. Among black women aged 55–64 years, the rate increased 42% from 10.0 in 2000 to 14.2 in 2008, before declining to 10.3 in 2015. Among white women aged 45–54 years, the rate decreased 53% from 1.9 in 2005 to 0.9 in 2015. Among white women aged 55–64 years, the rate did not change, remaining at about 0.8. Throughout the period, HIV disease death rates among black women were higher compared with rates among white women for both age groups.
Source: National Vital Statistics System. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data_access/vitalstatsonline.htm.
Reported by: Yelena Gorina, yag9@cdc.gov, 301-458-4241.
Suggested citation for this article: QuickStats: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Disease Death Rates Among Women Aged 45–64 Years, by Race and Age Group — National Vital Statistics System, United States, 2000–2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2017;66:1004. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6637a11.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All HTML versions of MMWR articles are generated from final proofs through an automated process. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.
- Page last reviewed: September 21, 2017
- Page last updated: September 21, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir