Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Extreme Obesity Among Adults: United States, 1960–1962 Through 2011–2012
by Cheryl D. Fryar, M.S.P.H.; Margaret D. Carroll, M.S.P.H.; and Cynthia L. Ogden, Ph.D., Division of Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
PDF Version (153 KB)
Results from the 2011–2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), using measured heights and weights, indicate that an estimated 33.9% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over are overweight, 35.1% are obese, and 6.4% are extremely obese. Body mass index (BMI), expressed as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2), is commonly used to classify overweight (BMI 25.0–29.9), obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30.0), and extreme obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 40.0).
Age-adjusted trends in obesity and overweight prevalence since 1988–1994 are shown in Table 1. It is also possible to examine trends since 1960 among adults aged 20–74 (Table 2). The age-adjusted sex-specific trends of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity are shown in the figure. Table 3 shows the age-adjusted estimates of obesity prevalence by race and Hispanic origin for men and women since 1988–1994.
The prevalence of obesity as measured by BMI among non-Hispanic Asian adults was much lower than that reported for non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, and Hispanic adults. Although BMI is widely used as a measure of body fat, at a given BMI level body fat may vary by sex, age, and race and Hispanic origin. In particular, research suggests that Asian persons may have more body fat than white persons, especially at lower BMIs, and that health risks may begin at a lower BMI among Asian persons compared with others.
NHANES, conducted by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), is a stratified, multistage probability sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population of the United States. The survey began oversampling non-Hispanic Asian persons in 2011–2012, and the total Hispanic population in 2007–2008. Beginning in 2007–2008, Mexican American persons were no longer oversampled but are included in the oversampled total Hispanic population.
A household interview and a physical examination are conducted for each survey participant. During the physical examination, conducted in a mobile examination center, height and weight are measured as part of a comprehensive set of body measurements. These measurements are taken by trained health technicians, using standardized measuring procedures and equipment. Observations for pregnant women and for persons missing a valid height or weight measurement were not included in the data analysis.
For additional information on NHANES methods, visit the NHANES methods page.
Figure
Figure. Trends in adult overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among men and women aged 20–74: United States, selected years 1960–1962 through 2011–2012
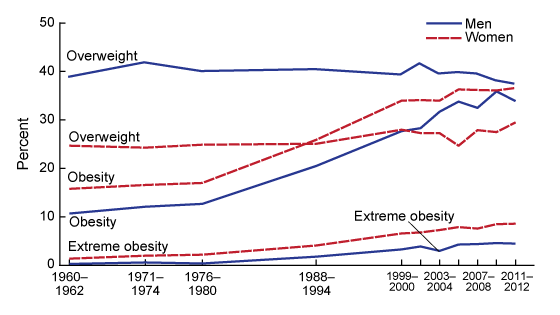
NOTES: Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. Pregnant females were excluded. Overweight is body mass index (BMI) of 25 or greater but less 30; obesity is BMI greater than or equal to 30; and extreme obesity is BMI greater than or equal to 40.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey 1960–1962; and National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1971–1974; 1976–1980; 1988–1994; 1999–2000, 2001–2002, 2003–2004, 2005–2006, 2007–2008, 2009–2010, and 2011–2012.
Tables
Table 1a. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults aged 20 and over: United States, selected years 1988–1994 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Sample (n) | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | ||||
| 1988–1994 | 16,235 | 33.1 (0.6) | 22.9 (0.7) | 2.8 (0.2) |
| 1999–2000 | 4,117 | 34.0 (1.0) | 30.5 (1.5) | 4.7 (0.6) |
| 2001–2002 | 4,413 | 35.1 (1.1) | 30.5 (1.1) | 5.1 (0.5) |
| 2003–2004 | 4,431 | 34.1 (1.1) | 32.2 (1.2) | 4.8 (0.6) |
| 2005–2006 | 4,356 | 32.6 (0.8) | 34.3 (1.4) | 5.9 (0.5) |
| 2007–2008 | 5,550 | 34.3 (0.8) | 33.7 (1.1) | 5.7 (0.4) |
| 2009–2010 | 5,926 | 33.0 (1.0) | 35.7 (0.9) | 6.3 (0.2) |
| 2011–2012 | 5,181 | 33.6 (1.3) | 34.9 (1.4) | 6.4 (0.6) |
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Crude estimates (not age-adjusted) for 2011–2012 are 33.9% overweight, 35.1% obese, and 6.4% extremely obese. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 1b. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among men aged 20 and over: United States, selected years 1988–1994 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||
| 1988–1994 | 40.7 (0.8) | 20.2 (0.7) | 1.7 (0.3) |
| 1999–2000 | 39.7 (1.4) | 27.5 (1.5) | 3.1 (0.7) |
| 2001–2002 | 42.2 (1.3) | 27.7 (1.0) | 3.6 (0.6) |
| 2003–2004 | 39.7 (1.5) | 31.1 (1.3) | 2.8 (0.4) |
| 2005–2006 | 39.9 (1.3) | 33.3 (2.0) | 4.2 (0.5) |
| 2007–2008 | 40.1 (1.4) | 32.2 (1.4) | 4.2 (0.5) |
| 2009–2010 | 38.4 (1.1) | 35.5 (1.7) | 4.4 (0.3) |
| 2011–2012 | 37.8 (1.5) | 33.5 (1.4) | 4.4 (0.9) |
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 1c. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among women aged 20 and over: United States, selected years 1988–1994 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||
| 1988–1994 | 25.9 (0.7) | 25.4 (0.7) | 3.9 (0.3) |
| 1999–2000 | 28.6 (1.6) | 33.4 (1.7) | 6.2 (0.7) |
| 2001–2002 | 28.2 (1.7) | 33.2 (1.5) | 6.5 (0.6) |
| 2003–2004 | 28.6 (1.2) | 33.2 (1.7) | 6.9 (0.9) |
| 2005–2006 | 25.5 (1.2) | 35.3 (1.4) | 7.4 (0.7) |
| 2007–2008 | 28.6 (1.2) | 35.4 (1.1) | 7.3 (0.6) |
| 2009–2010 | 27.9 (1.4) | 35.8 (0.9) | 8.1 (0.5) |
| 2011–2012 | 29.7 (1.8) | 36.1 (1.7) | 8.3 (0.7) |
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 2a. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults aged 20–74: United States, selected years 1960–1962 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Sample (n) | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | ||||
| 1960–1962 | 6,126 | 31.5 (0.5) | 13.4 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.1) |
| 1971–1974 | 12,911 | 32.7 (0.6) | 14.5 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.2) |
| 1976–1980 | 11,765 | 32.1 (0.6) | 15.0 (0.4) | 1.4 (0.1) |
| 1988–1994 | 14,319 | 32.6 (0.6) | 23.2 (0.7) | 3.0 (0.3) |
| 1999–2000 | 3,603 | 33.6 (1.1) | 30.9 (1.6) | 5.0 (0.6) |
| 2001–2002 | 3,916 | 34.4 (1.1) | 31.2 (1.1) | 5.4 (0.5) |
| 2003–2004 | 3,756 | 33.4 (1.2) | 32.9 (1.4) | 5.1 (0.6) |
| 2005–2006 | 3,835 | 32.2 (0.9) | 35.1 (1.5) | 6.2(0.5) |
| 2007–2008 | 4,876 | 33.6 (0.8) | 34.3 (1.2) | 6.0 (0.4) |
| 2009–2010 | 5,279 | 32.7 (1.0) | 36.1 (0.9) | 6.6 (0.3) |
| 2011–2012 | 4,674 | 33.3 (1.4) | 35.3 (1.4) | 6.6 (0.6) |
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. NHES 1960–1962 included adults aged 18–79, and NHANES 1971–1974 and 1976–1980 did not include individuals over age 74, so trend estimates are based on ages 20–74. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 2b. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among men aged 20–74: United States, selected years 1960–1962 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||
| 1960–1962 | 38.7 (0.7) | 10.7 (0.7) | *0.3 (0.1) |
| 1971–1974 | 41.7 (1.1) | 12.1 (0.6) | 0.6 (0.2) |
| 1976–1980 | 39.9 (0.8) | 12.7 (0.6) | 0.4 (0.1) |
| 1988–1994 | 40.3 (0.8) | 20.5 (0.7) | 1.8 (0.3) |
| 1999–2000 | 39.2 (1.5) | 27.7 (1.6) | 3.3 (0.7) |
| 2001–2002 | 41.5 (1.5) | 28.3 (1.1) | 3.9 (0.7) |
| 2003–2004 | 39.4 (1.5) | 31.7 (1.4) | 3.0 (0.4) |
| 2005–2006 | 39.7 (1.3) | 33.8 (2.2) | 4.3 (0.5) |
| 2007–2008 | 39.4 (1.4) | 32.5 (1.5) | 4.4 (0.5) |
| 2009–2010 | 38.0 (1.2) | 35.9 (1.7) | 4.6 (0.4) |
| 2011–2012 | 37.3 (1.5) | 33.9 (1.5) | 4.5 (1.0) |
* Estimate has a relative standard error greater than 30% and less than or equal to 40% and should be used with caution because it does not meet standards of reliability or precision.
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. NHES 1960–1962 included adults aged 18–79, and NHANES 1971–1974 and 1976–1980 did not include individuals over age 74, so trend estimates are based on ages 20–74.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 2c. Age-adjusted prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among women aged 20–74: United States, selected years 1960–1962 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Overweight | Obese | Extremely obese |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||
| 1960–1962 | 24.7 (0.8) | 15.8 (0.6) | 1.4 (0.2) |
| 1971–1974 | 24.3 (0.7) | 16.6 (0.6) | 2.0 (0.3) |
| 1976–1980 | 24.9 (0.8) | 17.0 (0.6) | 2.2 (0.3) |
| 1988–1994 | 25.1 (0.8) | 25.9 (1.0) | 4.1 (0.3) |
| 1999–2000 | 28.0 (1.7) | 34.0 (1.8) | 6.6 (0.7) |
| 2001–2002 | 27.3 (1.6) | 34.1 (1.6) | 6.8 (0.6) |
| 2003–2004 | 27.3 (1.3) | 34.0 (1.9) | 7.3 (1.0) |
| 2005–2006 | 24.7 (1.3) | 36.3 (1.5) | 7.9 (0.8) |
| 2007–2008 | 27.9 (1.2) | 36.2 (1.3) | 7.6 (1.0) |
| 2009–2010 | 27.5 (1.5) | 36.1 (0.9) | 8.5 (0.5) |
| 2011–2012 | 29.5 (2.0) | 36.6 (1.6) | 8.6 (0.7) |
NOTES: Overweight is body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25.0 kg/m2 and less than 30.0 kg/m2. Obese is BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m2. Extremely obese is BMI greater than or equal to 40.0 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60–74. NHES 1960–1962 included adults aged 18–79, and NHANES 1971–1974 and 1976–1980 did not include individuals over age 74, so trend estimates are based on ages 20–74. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health Examination Survey and National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 3a. Age-adjusted prevalence of obesity among men aged 20 and over, by race and Hispanic origin: United States, selected years 1988–1994 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Non-Hispanic white | Non-Hispanic black | Non-Hispanic Asian | Hispanic | Mexican American |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||||
| 1988–1994 | 20.3 (0.9) | 21.1 (1.0) | — | — | 23.9 (1.0) |
| 1999–2000 | 27.3 (1.8) | 27.9 (1.6) | — | — | 28.9 (1.9) |
| 2001–2002 | 29.0 (1.3) | 27.9 (2.0) | — | — | 25.9 (2.0) |
| 2003–2004 | 31.1 (1.5) | 34.0 (3.5) | — | — | 31.6 (2.5) |
| 2005–2006 | 33.0 (2.2) | 37.0 (2.4) | — | — | 27.0 (1.9) |
| 2007–2008 | 31.9 (1.9) | 37.2 (2.5) | — | 34.2 (3.0) | 35.8 (3.5) |
| 2009–2010 | 36.2 (2.1) | 38.8 (2.3) | — | 37.0 (2.2) | 38.6 (2.4) |
| 2011–2012 | 32.4 (1.3) | 37.1 (1.9) | 10.0 (1.6) | 40.1 (2.1) | 44.0 (2.6) |
— Data not available.
NOTES: Obesity is body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Table 3b. Age-adjusted prevalence of obesity among women aged 20 and over, by race and Hispanic origin: United States, selected years 1988–1994 through 2011–2012
| Survey period | Non-Hispanic white | Non-Hispanic black | Non-Hispanic Asian | Hispanic | Mexican American |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent (standard error) | |||||
| 1988–1994 | 22.9 (1.1) | 38.4 (1.4) | — | — | 35.4 (1.4) |
| 1999–2000 | 30.1 (2.1) | 49.5 (3.0) | — | — | 39.5 (3.9) |
| 2001–2002 | 31.2 (1.6) | 48.2 (2.7) | — | — | 37.0 (3.2) |
| 2003–2004 | 30.2 (2.1) | 53.9 (3.0) | — | — | 42.3 (2.7) |
| 2005–2006 | 32.9 (1.8) | 52.9 (2.1) | — | — | 42.1 (2.8) |
| 2007–2008 | 33.0 (1.8) | 49.4 (2.0) | — | 43.0 (2.6) | 45.1 (3.1) |
| 2009–2010 | 32.2 (1.4) | 58.5 (2.8) | — | 41.4 (2.0) | 44.9 (1.6) |
| 2011–2012 | 32.8 (2.7) | 56.6 (2.1) | 11.4 (2.2) | 44.4 (2.1) | 49.2 (3.4) |
— Data not available.
NOTES: Obesity is body mass index greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2. Age-adjusted by the direct method to the year 2000 U.S. Census Bureau estimates using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over. Pregnant females were excluded from the analysis.
SOURCE: CDC/NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
For more detailed estimates, see:
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 288(14):1723–7. 2002.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295(13):1549–55. 2006.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, McDowell MA, Flegal KM. Obesity among adults in the United States—No statistically significant change since 2003–2004 [PDF – 366 KB]. NCHS data brief no 1. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2007.
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 303(3):235–41. 2010.
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 307(5):491–7. 2012.
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA 311(8):806–14. 2014.
This Health E-Stat supersedes the earlier versions below:
- Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–1962 through 2009–2010
- Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–1962 through 2007–2008
- Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–62 through 2005–2006
- Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults: United States, 2003–2004
- Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults: United States, 1999–2002
- Page last reviewed: November 6, 2015
- Page last updated: September 19, 2014
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir