Diagnosis & Detection
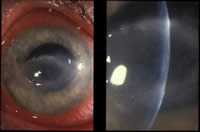
Eye of patient with Acanthamoeba keratitis. (Photo courtesy of Dan B. Jones, M.D. )
Print-and-Go Fact Sheet
Early diagnosis is essential for effective treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis. The infection is usually diagnosed by an eye specialist based on symptoms, growth of the ameba from a scraping of the eye, and/or seeing the ameba by a process called confocal microscopy.
Granulomatous Amebic Encephalitis (GAE) and disseminated infection are more difficult to diagnose and are often at advanced stages when they are diagnosed. Tests useful in the diagnosis of GAE include brain scans, biopsies, or spinal taps. In disseminated disease, biopsy of the involved sites (e.g. , skin, sinuses) can be useful in diagnosis.
More Information
For more information about laboratory diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection, see the DPDx Web site:
- Page last reviewed: July 27, 2017
- Page last updated: July 27, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
