Pathogen & Environment
Causal Agent:
Many species of Cryptosporidium exist that infect humans and a wide range of animals. Although Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium hominis (formerly known as C. parvum anthroponotic genotype or genotype 1) are the most prevalent species causing disease in humans, infections by C. felis, C. meleagridis, C. canis, and C. muris have also been reported.
Life Cycle
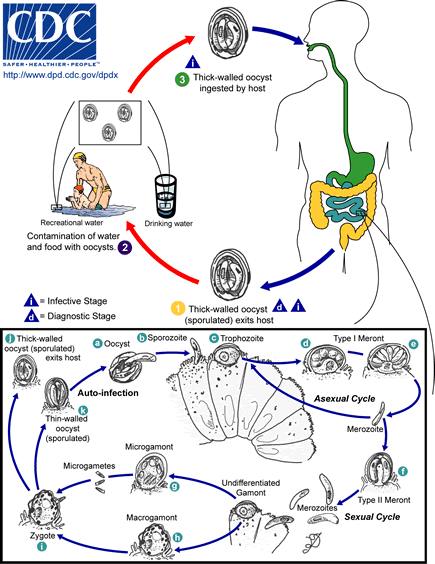
Sporulated oocysts, containing 4 sporozoites, are excreted by the infected host through feces and possibly other routes such as respiratory secretions ![]() . Transmission of Cryptosporidium parvum and C. hominis occurs mainly through contact with contaminated water (e.g., drinking or recreational water). Occasionally food sources, such as chicken salad, may serve as vehicles for transmission. Many outbreaks in the United States have occurred in waterparks, community swimming pools, and day care centers. Zoonotic and anthroponotic transmission of C. parvum and anthroponotic transmission of C. hominis occur through exposure to infected animals or exposure to water contaminated by feces of infected animals
. Transmission of Cryptosporidium parvum and C. hominis occurs mainly through contact with contaminated water (e.g., drinking or recreational water). Occasionally food sources, such as chicken salad, may serve as vehicles for transmission. Many outbreaks in the United States have occurred in waterparks, community swimming pools, and day care centers. Zoonotic and anthroponotic transmission of C. parvum and anthroponotic transmission of C. hominis occur through exposure to infected animals or exposure to water contaminated by feces of infected animals ![]() . Following ingestion (and possibly inhalation) by a suitable host
. Following ingestion (and possibly inhalation) by a suitable host ![]() , excystation
, excystation ![]() occurs. The sporozoites are released and parasitize epithelial cells (
occurs. The sporozoites are released and parasitize epithelial cells (![]() ,
, ![]() ) of the gastrointestinal tract or other tissues such as the respiratory tract. In these cells, the parasites undergo asexual multiplication (schizogony or merogony) (
) of the gastrointestinal tract or other tissues such as the respiratory tract. In these cells, the parasites undergo asexual multiplication (schizogony or merogony) (![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ) and then sexual multiplication (gametogony) producing microgamonts (male)
) and then sexual multiplication (gametogony) producing microgamonts (male) ![]() and macrogamonts (female)
and macrogamonts (female) ![]() . Upon fertilization of the macrogamonts by the microgametes (
. Upon fertilization of the macrogamonts by the microgametes (![]() ), oocysts (
), oocysts (![]() ,
, ![]() ) develop that sporulate in the infected host. Two different types of oocysts are produced, the thick-walled, which is commonly excreted from the host
) develop that sporulate in the infected host. Two different types of oocysts are produced, the thick-walled, which is commonly excreted from the host ![]() , and the thin-walled oocyst
, and the thin-walled oocyst ![]() , which is primarily involved in autoinfection. Oocysts are infective upon excretion, thus permitting direct and immediate fecal-oral transmission.
, which is primarily involved in autoinfection. Oocysts are infective upon excretion, thus permitting direct and immediate fecal-oral transmission.
- Page last reviewed: February 20, 2015
- Page last updated: February 20, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir