STDs in Women and Infants Figures
This web page is archived for historical purposes and is no longer being updated. Newer data is available on the STD Data and Statistics page.
- Page last reviewed: January 7, 2014 (archived document)
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
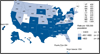 Figure A. Chlamydia—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012
Figure A. Chlamydia—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012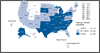 Figure B. Gonorrhea—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012
Figure B. Gonorrhea—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012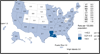 Figure C. Primary and Secondary Syphilis—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012
Figure C. Primary and Secondary Syphilis—Women—Rates by State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012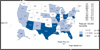 Figure D. Congenital Syphilis—Infants—Rates by Year of Birth and State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012
Figure D. Congenital Syphilis—Infants—Rates by Year of Birth and State, United States and Outlying Areas, 2012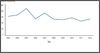 Figure F. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease—Initial Visits to Physicians’ Offices by Women Aged 15–44 Years, United States, 2003–2012
Figure F. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease—Initial Visits to Physicians’ Offices by Women Aged 15–44 Years, United States, 2003–2012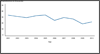 Figure G. Ectopic Pregnancy—Hospitalizations of Women Aged 15–44 Years, United States, 2001–2010
Figure G. Ectopic Pregnancy—Hospitalizations of Women Aged 15–44 Years, United States, 2001–2010