Rates of TBI-related Hospitalizations by Age Group — United States, 2001–2010
Changes in the rates of TBI-related hospitalizations vary depending on age. For persons 44 years of age and younger, TBI-related hospitalizations decreased between the periods of 2001–2002 and 2009–2010. However, rates for age groups 45–64 years of age and 65 years and older increased between these time periods. Rates in persons 45–64 years of age increased almost 25% from 60.1 to 79.4 per 100,000. Rates of TBI-related hospitalizations in persons 65 years of age and older increased more than 50%, from 191.5 to 294.0 per 100,000 during the same period, largely due to a substantial increase (39%) between 2007–2008 and 2009–2010. In contrast, rates of TBI-related hospitalizations in youth 5–14 years of age fell from 54.5 to 23.1 per 100,000, decreasing by more than 50% during this period.
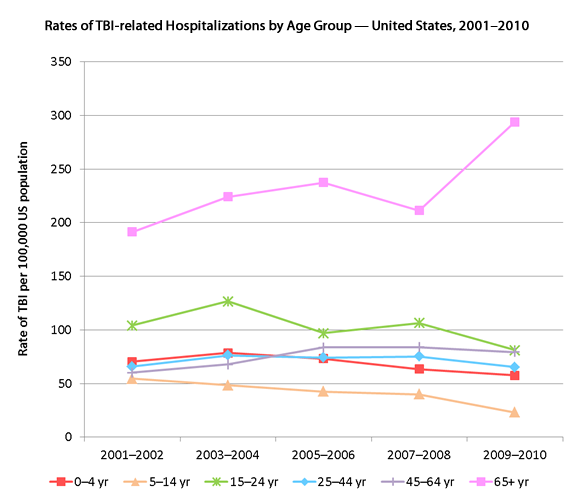
| 0–4 yr | 5–14 yr | 15–24 yr | 25–44 yr | 45–64 yr | 65+ yr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4 yr | 5–14 yr | 15–24 yr | 25–44 yr | 45–64 yr | 65+ yr | |
| 2001–2002 | 70.3 | 54.5 | 104.1 | 65.9 | 60.1 | 191.5 |
| 2003–2004 | 78.7 | 48.5 | 126.6 | 76.4 | 67.9 | 224.2 |
| 2005–2006 | 73.3 | 42.5 | 97.1 | 74.2 | 83.7 | 237.5 |
| 2007–2008 | 63.4 | 40.0 | 106.5 | 75.2 | 83.9 | 211.4 |
| 2009–2010 | 57.7 | 23.1 | 81.2 | 65.3 | 79.4 | 294.0 |
Source:
- National Hospital Discharge Survey — United States, 2001–2010 (Hospitalizations)
- Page last reviewed: January 22, 2016
- Page last updated: January 22, 2016
- Content source:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
- National Center for Injury Prevention and Control,
- Division of Unintentional Injury Prevention


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir
