Transmission
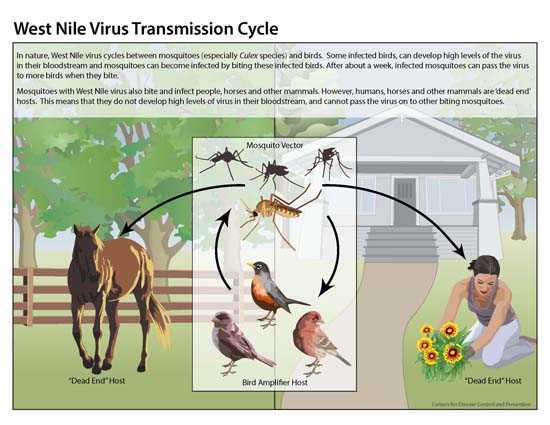
West Nile virus is most commonly transmitted to humans by mosquitoes.
Additional routes of human infection have also been documented. It is important to note that these methods of transmission represent a very small proportion of cases:
- Blood transfusions
- Organ transplants
- Exposure in a laboratory setting
- From mother to baby during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding
West Nile virus is not transmitted:
- From person-to-person or from animal-to-person through casual contact. Normal veterinary infection control precautions should be followed when caring for a horse suspected to have this or any viral infection.
- From handling live or dead infected birds. You should avoid bare-handed contact when handling any dead animal. If you are disposing of a dead bird, use gloves or double plastic bags to place the carcass in a garbage can.
- Through consuming infected birds or animals. In keeping with overall public health practice, and due to the risk of known food-borne pathogens, always follow procedures for fully cooking meat from either birds or mammals.
Transmission cycle
- Page last reviewed: February 12, 2015
- Page last updated: July 11, 2017
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir