We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Aphthous stomatitis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Affects 20% of the normal population
- Unclear etiology
- Resolve spontaneously in 10-14d
Clinical Features
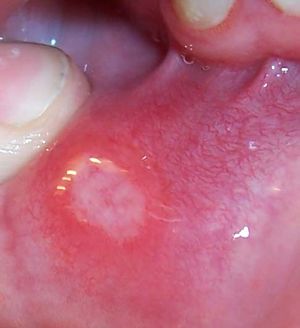
- Involves the nonkeratinized epithelium (especially labial and buccal mucosa)
- Begins as erythematous macule that ulcerates and forms a central fibropurulent eschar
- Lesions measure from 2-3mm to several cm in diameter
Differential Diagnosis
Oral rashes and lesions
- Angioedema
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Herpes gingivostomatitis
- Herpes labialis
- Measles (Koplik's spots)
- Perioral dermatitis
- Oral thrush
- Steven Johnson syndrome
- Strep pharyngitis
Evaluation
Management
- Topical corticosteroids
- Betamethasone syrup OR
- Dexamethasone 0.01% elixir as mouth rinse OR
- Fluocinonide 0.05% gel applied topically to isolated lesions
Disposition
See Also
References
Authors
Jordan Swartz, Ross Donaldson, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer