We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Box jellyfish
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- cnidarian invertebrates distinguished by their cube-shaped medusae
- "Chironex fleckeri" cause of most deaths
- largely restricted to the Indo-Pacific Ocean/Australian waters but various species can be found widely
- most stings are benign (local treatment only), only a few species have been implicated in human deaths
Mechanism
- specific venom components unclear
- thought to affect sodium/potassium/calcium channels
- Chironex fleckeri venom causes cell membranes to become porous allowing K+ influx/hyperkalemia
Clinical Features
- stings associated with immediate pain, lasting up to 8 hours, and linear welts in a cross-hatched pattern
- may progress to blisters/necrosis
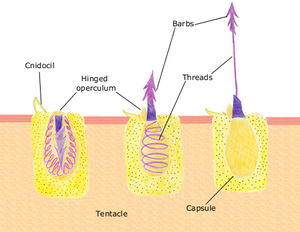
- 25-30% may still have tentacles attached
- systemic envenomation (usually >10% BSA) can manifest as cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory dysfunction, death
- usually manifests within 5 minutes of sting
- delayed hypersensitivity reactions occur in >50%
- itching, redness at sting sites 7-14d after initial incidence
Differential Diagnosis
Marine toxins and envenomations
- Toxins
- Stingers
- Venomous fish (catfish, zebrafish, scorpion fish, stonefish)
- Lionfish
- Sea urchins
- Cone shells
- Nematocysts
- Jellyfish (Cnidaria)
- Box jellyfish
- Portuguese man-of-war
- Coral reef
- Fire Corals
- Sea anemones
- Sea wasps
- Jellyfish (Cnidaria)
- Bites
Evaluation
- Generally a clinical diagnosis
Management
- pain control
- pour liberal amounts of vinegar and remove any tentacles
- tentacles separated from medusae can still emit venom
- supportive measures for minor envenomations (ice recommended but heat may actually work better)
- antihistamines and steroids for hypersensitivity reaction
- do NOT pressure bandage
- antivenom for life-threatening envenomations
- ovine IgG Fab with 20,000 units/ampule
Antivenom Indications^
- cardiac arrest
- undiluted antivenom administered as an IV Push: up to 6 vials
- if no response then give magnesium IV
- hypotension, tachycardia, shock, arrhythmia
- dilute 3 amps antivenom in 100mL NS and run over 20 minutes
- can repeat for a total of 6 vials
- intractable pain
- give 1 amp diluted in 100mL NS run over 20 minutes
^anti-venom can cause serum sickness 4-14 days after administration
Disposition
See Also
References
- Bastian Bentlage, Paulyn Cartwright, Angel A. Yanagihara, Cheryl Lewis, Gemma S. Richards and Allen G. Collins.Evolution of box jellyfishes (Cnidaria: Cubozoa), a group of highly toxic invertebrates. Proceedings of the Royal Society, November 18, 2009 DOI:10.1098/rspb.2009.1707
- Currie BJ, Jacups SP. Prospective study of Chironex fleckeri and other box jellyfish stings in the “Top End” of Australia’s Northern Territory. Med J Aust 2005; 183: 631-636
- Hughes RJ, Angus JA, Winkel KD, Wright CE. A pharmacological investigation of the venom extract of the Australian box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri, in cardiac and vascular tissues. Toxicol Lett. 2012 Feb 25;209(1):11-20. Epub 2011 Dec 2.
- http://www.toxinology.com/generic_static_files/cslavh_antivenom_boxjelly.html