We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Undifferentiated shock
From WikEM
(Redirected from Shock)
Contents
Undifferentiated HypotensionAlgorithm[1]
Check/manage the following in order:
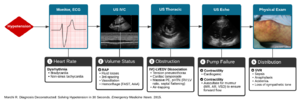
Algorithm for the Evaluation of Hypotension(By Dr. Ravi Morchi)
- Pulse (assess based on patient's age)
- Too slow or too fast (to the point where CO is affected)?
- If so, HR is likely primary etiology of hypotension
- Pace or cardiovert
- Too slow or too fast (to the point where CO is affected)?
- Volume Status
- What is the LV end-diastolic volume?
- Approximated by the IVC diameter or CVP
- If low:
- What is the LV end-diastolic volume?
- Contractility
- Is the myocardium severely depressed in its contractile function (cardiogenic shock)?
- Assess via ultrasound
- Treat with inotrope
- Is forward flow occurring?
- Assess for valvular dysfunction (MR, AR)
- Assess for obstruction (PE, tamponade)
- Is the myocardium severely depressed in its contractile function (cardiogenic shock)?
- Systemic Vascular Resistance
- Pathologic vasodilation (decreased SVR) suggested by:
- Warm extremities
- Bounding pulse
- Treated based on likely etiology of distributive shock (see below)
- Pathologic vasodilation (decreased SVR) suggested by:
Differential Diagnosis
Shock
- Cardiogenic
- Acute valvular Regurgitation/VSD
- CHF
- Dysrhythmia
- ACS
- Myocardial Contusion
- Myocarditis
- Drug toxicity (e.g. beta blocker, CCB, or bupropion OD)
- Obstructive
- Distributive
- Hypovolemic
- Severe dehydration
- Hemorrhagic shock (traumatic and non-traumatic)
Evaluation
Shock index (SI)[2]
SI = HR / SBP
- Used when HR and SBP do not predict severity of hypovolemia in early stages
- May be used as secondary triage tool in mass casualty incidents[3]
- 0.5-0.7 is normal
- >0.70-0.75 for occult shock or requirement of life-saving intervention
Management
- Treat underlying type
Vasopressors
| Pressor | Initial Dose | Max Dose | Cardiac Effect | BP Effect | Arrhythmias | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dobutamine | 2.5 mcg/kg/min | 10-40 mcg/kg/min | mainly inotrope (ß1) | alpha effect minimal | Some HR(ß1) increase. Also Increase SA and AV node fx | Debut Research 1979[4] Isoproterenol has most Β2 vasodilatory and Β1 HR effects |
| Dopamine | 2 mcg/kg/min | 20-50 mcg/kg/min | β1 and NorEpi release | α effects if > 20mcg/kg/min | Arrhythmogenic from β1 effects | More adverse events when used in shock compared to Norepi[5] |
| Epinepherine | 0.1-1 mcg/kg/min | |||||
| Norepinephrine | 8-12 mcg/min | 30 mcg/min | β1 direct effect | β1 and α1,2 effects | Less arrhythmias than Dopamine[5] | Increases MAP, coronary perfusion pressure, little β2 effects. |
| Milrinone | 50 mcg/kg x 10 min | 0.375-75 mcg/kg/min | Direct influx of Ca2+ channels | Smooth muscle vasodilator | PDE Inhibitor which increases Ca2+ uptake by sarcolemma. No venodilatory activity | |
| Phenylephrine | 100-180 mcg/min then 40-60 mcg/min | 0.4-9 mcg/kg/min | Alpha agonist | Long half life | ||
| Vasopressin | Fixed Dose | 0.4 U/min | unknown | increases via ADH peptide | should not be titrated due to ischemic effects | |
| Methylene blue[6] | IV bolus 2 mg/kg over 15 min | 1-2 mg/kg/hour | Possible increased inotropy, cardiac use of ATP | Inhibits NO mediated peripheral vasodilation | Don't use in G6PD deficiency, ARDS, pulmonary hypertension |
| Medication | IV Dose (mcg/kg/min) | Concentration |
| Norepinephrine (Levophed) | 0.1-2 mcg/kg/min | 8mg in 500mL D5W |
| Dopamine | 2-20 mcg/kg/min | 400mg in 250 D5W |
| Dobutamine | 2-20 mcg/kg/min | 250mg in 250 mg D5W |
| Epinephrine | 0.1-1 mcg/kg/min | 1mg in 250 D5W |
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Morchi R. Diagnosis Deconstructed: Solving Hypotensionin 30 Seconds. Emergency Medicine News. 2015.
- ↑ Levitan, Richard M. Fundamentals of Airway Management. 3rd ed. Irving, TX: Emergency Medicine Residents' Association, 2015.
- ↑ Vassallo J et al. Usefulness of the Shock Index as a secondary triage tool. J R Army Med Corps. 2015 Mar;161(1):53-7.
- ↑ Edmund H. Sonnenblick, M.D., William H. Frishman, M.D., and Thierry H. LeJemtel, M.D. Dobutamine: A New Synthetic Cardioactive Sympathetic Amine
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 De Backer Daniel et al. Comparison of Dopamine and Norepinephrine in the Treatment of Shock. NEJM 363(9). 779-789
- ↑ Pasin L et al. Methylene blue as a vasopressor: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Crit Care Resusc. 2013 Mar;15(1):42-8.
Video
