We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Cardiac ultrasound
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Important to realize that the cardiac ultrasound preset on some machines reverses the indicator marking with the probe indicator on the right
- With the general ED ultrasound the probe indicator is on the left of the screen
Indications
Technique
- Select probe
- Phased array probe
- Location
Parasternal Long
- Pointer to the left hip, probe at left 3rd/4th intercostal space adjacent to sternum
- Use to visualize global function and rule out pericardial effusion/tamponade
- Can evaluate mitral valve, aortic valve, aortic root, LV squeeze
Parasternal Short
- Pointer to left shoulder, probe at left 3rd/4th intercostal space adjacent to sternum
- Tip: obtain parasternal long view, then rotate probe 90 degrees
- Use to evaluate LV squeeze, right ventricle
- Right heart strain = dilated right ventricle
Apical 4 chamber
- Pointer to right, usually below nipple
- Use to visualize global function (Left and right ventricle, squeeze)
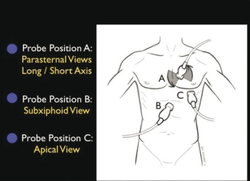
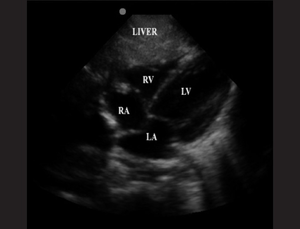
Subxyphoid
- Pointer to right, subxyphoid with probe pointed toward head
- Use liver to as acoustic window to visualize heart
Suprasternal (Optional)
- Pointer at 12 o'clock (cephalad) and place in sternal notch
- Move probe inferior and to the left to visualize aortic arch
- Rotate probe clockwise for further image optimization
- Can evaluate for aortic dissections/aneurysms, coarctation of the aorta, and aortic stenosis/regurgitation
Apical 5 chamber (optional)
- Start in the Apical 4 chamber view, tilt the probe upwards until the aortic outflow tract is seen
- This view can be used to calculate the velocity time integral (VTI) and subsequently cardiac output to assess fluid responsiveness
Apical 3 chamber (optional)
- Start in the Apical 4 chamber view, rotate the probe until the marker points towards the patient's right shoulder
- This view can be used to calculate the velocity time integral (VTI) and subsequently cardiac output to assess fluid responsiveness (alternate method to the apical 5 chamber view)
Findings
Classic Ultrasound Findings For Critically Ill Patients
| Disease | Cardiac | IVC | Lung (Phased Array) | Lung (Linear) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MI | Focal WMA Mod/Poor squeeze |
↑ | NL or B-lines | Sliding |
| Tamponade | RA collapse with filling RV collapse with filling |
↑ | NL | Sliding |
| pneumothorax | NL or Hyperdynamic | ↑ | Lung point Consolidated lung |
Absent lung sliding |
| Sepsis | Hyperdynamic squeeze | ↓ | NL (see pneumonia) | Sliding |
| Pneumonia | Hyperdynamic squeeze | NL or ↓ | Unilateral B-lines | Sliding |
| Decompensated HF | Mod/Poor squeeze | ↑ | Bilateral B-lines | Sliding |
| PE | RV > LV McConnell's sign |
↑ | NL or Unilateral B-lines | Sliding |
Parasternal Long
- Assess for percardial effusion and differentiate from pleural effusions
- Assess squeeze using E-point septal separation (EPSS)
- EPSS >7mm is 100% sensitive for EF <30%[1]
Parasternal Short
- Assess for pericaridal effusion
- Assess for squeeze - visual estimate of hyperdynamic, good, moderate, or poor
Apical 4 chamber
- Assess RV:LV diameter at the level of the valves
- Normal RV:LV is 0.6:1
- RV strain is >1:1
- Assess for McConnell's sign
Subxyphoid
- Assess for pericardial effusion
- If concerns for PE, assess for right ventricular wall diameter in end diastole[2]
- Diameter of <5mm is suggestive of acute pulmonary hypertension
- Diameter of >5mm is suggestive of chronic pulmonary hypertension
Suprasternal (Optional)
- Assess for aortic dissection
IVC ultrasound
- Tyically included in interpretation
Images
Pearls and Pitfalls
Documentation
Normal Exam
A bedside ultrasound was conducted to assess the heart with clinical indications of SOB. The parasternal long, parasternal short, apical four chamber, subxyphoid, and IVC views were obtained. Normal diameter AOFT, no pericardial or pleural effusions identified, good squeeze, RV<LV, and IVC was not plethoric nor flat. Normal cardiac ultrasound.
Abnormal Exam
A bedside ultrasound was conducted to assess the heart with clinical indications of SOB. The parasternal long, parasternal short, apical four chamber, subxyphoid, and IVC views were obtained. Normal diameter AOFT, EPSS >7mm, no pericardial effusion, bilateral pleural effusions, poor squeeze, RV<LV, and IVC was plethoric. Indicative of systolic heart failure.
Clips
Video
See Also
References
- ↑ McKaigney CJ, Krantz MJ, La Rocque CL, et al. E-point septal separation: a bedside tool for emergency physician assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction. Am J Emerg Med. 2014; 32(6):493-497.
- ↑ Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23(7):685-713.