We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Hypocalcemia
From WikEM
Contents
Background
Serum Levels
- Low <8.5 (<2.0 ionized)
- Low! <6.5 (<1.5 ionized)
- Correct for hypoalbumimia
- Corrected Ca = (0.8 *(Normal Alb - Patient's Alb)) + Serum Ca
Fraction[1]
- 15% bound to anions (phosphate, lactate, citrate)
- 40% bound to albumin
- 45% free (regulated by PTH, Vit-D)
Causes
- Misc
- Shock
- Sepsis
- Pancreatitis
- Hypomag
- Rhabdo (phosphate overload)
- Massive transfusion
- Systemic Hydrofluoric Acid toxicity
- DiGeorge syndrome
- Decreased absorption
- Increased excretion
- Endocrine
- Drugs
- Cimetidine
- Phenytoin
- Lasix, loop diuretics
- Norepinephrine
- Glucagon
- Glucocorticoids
- Magnesium sulfate
- Nitroprusside
Clinical Features
- Paresthesias (mouth, fingertips)
- ↑ DTRs
- Cramps
- Weakness
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Chvostek/Trousseau signs, Tetany
- Hallucinations
- Laryngospasm
- Bronchospasm
- Cardiac dysrhythmias
Differential Diagnosis
Jaw Spasms
- Dystonic reaction
- Acute tetanus
- Conversion disorder
- Mandibular dislocation
- Electrolyte abnormality
- Hypocalcemic tetany
- Magnesium
- Meningitis
- Seizure disorder
- Strychnine poisoning
- Akathisia
- Stroke
- Drug toxicity (anticholinergic, phenytoin, valproate, carbamazepine)
- Torticollis
- PTA
- Rabies
- TMJ
Evaluation
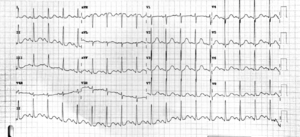
ECG
- QT Prolongation via increasing the ST length
- Only hypothermia and hypocalcemia prolong QT this way
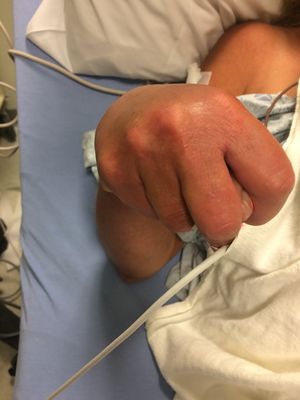
Trousseau's Sign (Mod to high SN and SP)
- Inflate BP cuff for 2-3 mins
- Positive = Muscle contractions of the hand and wrist
Chvostek's Sign (Low SN and SP)
- Tapping on the face just anterior to the ear and just below the zygomatic bone
- Positive = Ipsilateral facial twitching
Labs
- BMP
- Mag, Phos
- PTH (secondary hyperparathyroidism)
Management
Avoid empiric treatment in patients taking digoxin due to risk for Stone Heart
- Asymptomatic
- Calcium gluconate 1 gm PO Q6hrs
- Vitamin D (calcitriol) 0.2 mcg BID
- Symptomatic
- Calcium gluconate/chloride 10mL of 10% soln IV over 10min
- Correct hypomag at same time (otherwise PTH is inhibited)
Disposition
- Admit all symptomatic patients
See Also
References
- ↑ Yu, AS. Relation between total and ionized serum calcium concentrations. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on October 6th, 2016.)
Video