We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Lichen sclerosus
From WikEM
Contents
Background
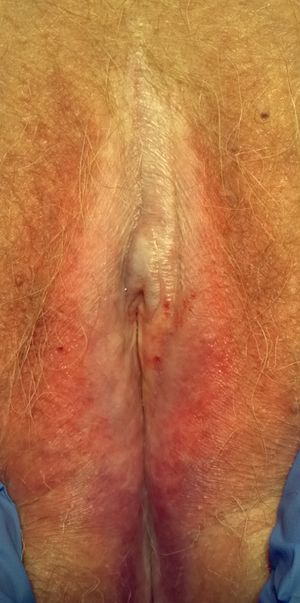
- A benign, chronic, progressive dermatologic condition characterized by marked inflammation, epithelial thinning, and distinctive dermal changes accompanied by symptoms of pruritus and pain
- Typically affects postmenopausal women, however it does sometimes occur in men, children, and premenopausal women
- Thought to be related to low estrogen states
Clinical Features
- Skin becomes thin, wrinkles, and whitened
- Most common symptoms include itching and pain at the affected areas, most commonly the clitoris and labia (although any skin surface can be affected)
- Other symptoms include anal discomfort, dyspareunia, and dysuria
Differential Diagnosis
Vulvovaginitis
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Candida vaginitis
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Contact vulvovaginitis
- Atrophic vaginitis
- Lichen sclerosus
- Tinea cruris
- Chlamydia/Gonorrhea infection
Evaluation
- Biopsy — A vulvar punch biopsy is taken to demonstrate atypical cell histology
- Histopathology — Epidermis is thinned, areas of hyperkeratosis may be observed. Early lesions may show irregular epidermal acanthosis
- Clinical judgment should guide the diagnosis and treatment of LS when biopsy results are not specific
Management
- Behavioral changes: good hygiene, avoid scratching area
- topical steroids such as clobetasol proprionate
Disposition
- Can be chronic
- Increases chance of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma