We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Psoriasis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Often begins in the 2nd or 3rd decade of life
- Chronic and relapsing
Triggers
- Stress
- Trauma
- Drugs
Clinical Features
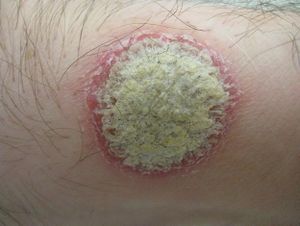
- Well-demarcated erythematous plaques and papules with silvery white scales
- Epidermal hyperproliferation
- Commonly found on the trunk, scalp, nail pitting, and extensor surfaces
- Auspitz sign: plaque removal reveals pinpoint-bleeding areas
- Associated with psoriatic arthritis, especially in nail involvement
Differential Diagnosis
Rash
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Allergic reaction
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Cellulitis
- Chickenpox
- Chikungunya
- Coxsackie
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Drug rash
- DRESS syndrome
- Erysipelas
- Erythema multiforme
- Exfoliative erythroderma
- Henoch-schonlein purpura
- Hives
- Impetigo
- Measles
- Miliaria (Heat Rash)
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Pellagra
- Petechiae & Purpura
- Poison Oak, Ivy, Sumac
- Psoriasis
- Pityriasis rosea
- Scabies
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Serum Sickness
- Smallpox
- Shingles
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Tinea capitus
- Tinea corporis
- Vitiligo
Management
- Ketoconazole 2% shampoo
- Hydrocortisone cream 1%
- Systemic steroids should be avoided due to the risk of developing rebound or induction of pustular psoriasis
See Also
References
- Uptodate
- Hess MR, Hess SP: Skin Disorders Common on the Trunck, in Tintinalli JE, Kelen GD, Stapczynski JS (eds): Emergency Medicine, A Comprehensive Study Guide, ed 7. New York, McGraw-Hill, 2011, (Ch) 249:p 1653-1654
Authors
Aaron Snyder, Ross Donaldson, Kevin Lu, Daniel Ostermayer, Neil Young