We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Multifocal atrial tachycardia
From WikEM
Contents
Background
- Multiple (3 or more) ectopic foci in the atria causing an irregular atrial tachycardia
- Increased automaticity due to causes listed below
Causes
- COPD
- CHF
- Sepsis
- Methylxanthine toxicity
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Other associations
- Valvular heart disease
- DM
- Acute renal failure
- Postoperative state
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- Anemia
Clinical Features
- Palpitations
- Dyspnea
- Chest pain
- Presyncope/syncope
Differential Diagnosis
Palpitations
- Arrhythmias:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Grouped beats on ECG (commonly misdx as A-fib)
- Atrial bigeminy and trigeminy
- Mobitz I or Mobitz II
- Atrial flutter
- SVT
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- PVCs
- Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPW)
- Sinus node dysfunction
- AV Block
- Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Non-arrhythmic cardiac causes:
- Cardiomyopathy
- CHF
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Congenital heart disease
- Pericarditis
- Valvular disease
- Pacemaker malfunction
- Acute MI
- Psychiatric causes:
- Drugs and Medications:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Meds (i.e. digitalis, theophylline)
- Street drugs (i.e. cocaine)
- Tobacco
- Misc
Evaluation
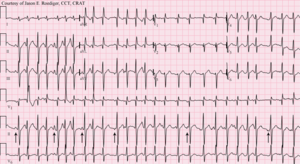
- ECG
- Irregular tachycardia (>100 bpm)
- At least 3 distinct p wave morphologies
- No dominant pacemaker site
- BMP, Magnesium
- hemoglobin/hematocrit
- Consider infectious disease work up
- Consider ABG/VBG
Management
- Treat the underlying cause
- Replace magnesium
- Replace potassium
- Increased AV nodal activity is unlikely to be effective
- Vagal maneuvers and adenosine may help reveal underlying rhythm/p-waves
- Can consider BB/CCB in hemodynamically stable patient (caution with pulmonary disease)
- Cardioversion not definitive, likely recurrence if underlying illness not addressed
Disposition
- Disposition depends on the underlying illness, but often requires admission due to illness severity/age
- Poor prognostic sign when developed during hospitalization/illness
- 60% in hospital mortality
- mean survival around 1 year
- Due to illness not arrhythmia
See Also
External Links
References
Authors
Colin Hoff, Kevin Lu, Ross Donaldson, Neil Young, Claire, Daniel Ostermayer