We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Osgood-Schlatter disease
From WikEM
Contents
Background
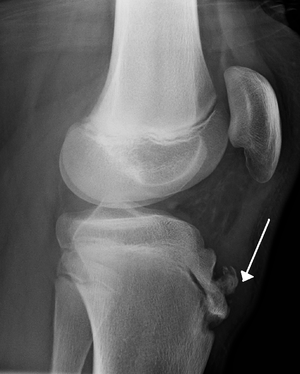
- Apophysitis of tibial tubercle resulting from repeated normal stresses or overuse
- Patients are usually 10-15yr old
- More commonly occurs in running or jumping athletes
- Most cases are bilateral
- Although symptoms are commonly asymmetric
Evaluation
- Chronic, intermittent pain over the anterior aspect of knee and tibial tuberosity
- Pain aggravated by activity, improves with rest
- Prominence and soft tissue swelling over tibial tubercle
- Imaging is not necessary
- If obtained shows nonspecific irregularities of tibial tubercle
- If initial presentation includes swelling, inability to actively extent the knee, decreased strength with knee extension, or inability to walk, obtain radiograph to evaluate for avulsion fracture of the tibial epiphysis
Differential Diagnosis
Knee diagnoses
Acute Injury
- Knee fractures
- Patella fracture
- Tibial plateau fracture
- Knee dislocation
- Patella dislocation
- Segond fracture
- Meniscus and ligament knee injuries
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's knee)
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
Nontraumatic/Subacute
- Septic Joint
- Gout
- Popliteal cyst (Baker's)
- Prepatellar bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Pes anserine bursitis
- Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumper's knee)
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Arthritis
Management
- Disease is self-limited
- Most patients' symptoms respond to rest and temporary avoidance of offending activity
- Complete avoidance of activity is not essential
- Immobilization is contraindicated
- NSAIDs
- Apply ice after activity
Disposition
Discharge