We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Rheumatoid arthritis
From WikEM
(Redirected from RA)
Contents
Background
- Erosive polyarthritis
Clinical Features
- Morning stiffness
- Polyarthritis of MCP and PIP joints
- Does NOT involve DIP joints
- Wrists, elbows, shoulders, ankles, knees also commonly involved
- Ulnar deviation at the wrist
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Most patients initially diagnosed in the early 50s
- Common associated conditions in severe cases: pleuritis, interstital lung disease, pericarditis, inflammatory eye disease
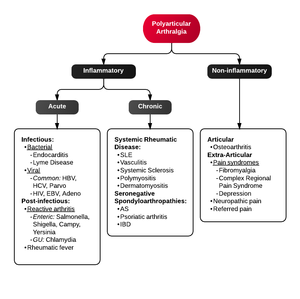
Differential Diagnosis
Polyarthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Serum sickness
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Serum sickness–like reactions
- Viral arthritis
Evaluation
- Xray affected joints for erosions
- Rheumatoid factor (positive in 60% to 70% of patients)
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodies (positive in about 70% of patients)
- ANA
- Consider arthrocentesis
- WBC count typically 1,500-20,000
Management
- NSAIDs
- Symptomatic relief without slowing underlying disease
- Glucocorticoids
- Consider intraarticular injection if a single joint is inflammed
- Systemic steroids reserved for moderate-severe flairs
- Opiods have a limited role
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)
- Can be started by primary care provider or rheumatologist after ER visit
Disposition
- Refer to primary care provider or rheumatologist