We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Reactive arthritis
From WikEM
Contents
Background
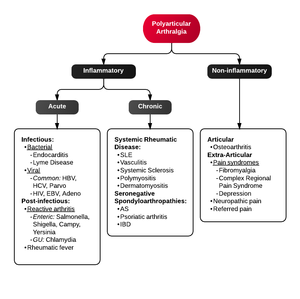
- Seronegative spondyloarthropathy that manifests as an acute, asymmetric, oligoarthritis (LE>UE) that occurs 2-6 weeks after infection
- Associated with bacterial infections
- Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, etc.
- Classic triad: urethritis, conjunctivitis, and arthritis ("Can't pee, can't see, can't climb a tree")
Clinical Features
- Preceding Infection
- Urethritis: generally caused by Chlamydia or Ureaplasma
- Enteritis: generally caused by Salmonella or Shigella
- Preceding infection may be clinically silent
- Musculoskeletal symptoms
- Arthritis: oligoarthritis, usually in the lower extremities
- Enthesitis (pain at insertion sites)
- Dactylitis (sausage digits)
- Low back pain
- Extraarticular symptoms
- Conjunctivitis (less frequently uveitis, keratitis)
- GU symptoms
- Oral lesions
- Cutaneous and nail changes
- Keratoderma blennorrhagicum[1]
- Develops in 15% of patients
- Found on palm/soles. Vesicles/pustules with yellow/brown color. Appears similar to pustular psoriasis
Differential Diagnosis
Monoarticular arthritis
- Acute osteoarthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Crystal-induced (Gout, Pseudogout)
- Gonococcal septic arthritis
- Nongonococcal septic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Malignancy
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Trauma-induced arthritis
Oligoarthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Polyarthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Serum sickness
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Serum sickness–like reactions
- Viral arthritis
Migratory Arthritis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Rheumatic fever
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Viral arthritis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
- Must exclude gonococcal arthritis and other mimics
Management
- Treat inciting infection
- Symptomatic treatment of arthritis
- NSAIDs are first line (naproxen, diclofenac, indomethacin)
- Intraarticular and systemic steroids for NSAID refractory
Disposition
- Outpatient follow up, with DMARDs if refractory to NSAIDs
- 70% self-limited disease
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. The Skin in Immune, Autoimmune, and Rheumatic Disorders. In: Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. eds. Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology, 7e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
Authors
Michael Holtz, Daniel Eggeman, Kevin Lu, Amr Badawy, Neil Young, Daniel Ostermayer