We need you! Join our contributor community and become a WikEM editor through our open and transparent promotion process.
Sexually transmitted diseases
From WikEM
(Redirected from STI)
Contents
Background
- STD Prevalence: HPV> HSV-2 > Trichomonas > Chlamydia > HIV > HBV > Gonorrhea > Syphillis
- STD New infections: HPV > Chlamydia > Trichomonas > Gonorrhea > HSV-2 > Syphillis > HIV > HBV [1]
- It is important to treat sexual partners for all STDs
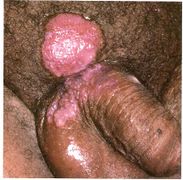
Visual Diagnosis
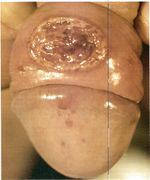
Primary Syphilis
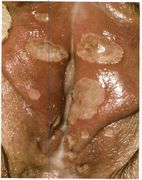
Bacterial Vaginosis
First Line Therapy[2]
- Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID for 7 days OR
- Metronidazole gel 0.75%, one full applicator (5 g) intravaginally, qd for 5 days OR
- Clindamycin cream 2%, one full applicator (5 g) intravaginally qHS for 7 days
Alternative Regimin
- Tinidazole 2 g PO qd for 2 days OR
- Tinidazole 1 g PO qd for 5 days OR
- Clindamycin 300 mg PO BID for 7 days OR
- Clindamycin ovules 100 mg intravaginally qHS for 3 days (do not use if patient has used latex condom in last 72 hrs)
Pregnant
- Metronidazole 250mg PO q8h x 7 days[3]
- Metronidazole 2g PO x 1 dose is also acceptable[3]
- Multiple studies have not demonstrated teratogenicity from metronidazole use[3]
Prophylaxis (Sexual Assault)
- Metronidazole 2 g PO x 1 OR
- Tinidazole 2 g PO x 1
Cervicitis/Urethritis
treatment cover gonorrhea and chlamydia jointly
- Male: Urethritis with discharge or simply dysuria
- Female: purulent discharge
Uncomplicated Infection
- Ceftriaxone 250mg IM once PLUS
- Azithromycin 1g PO once OR
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 7 days
Partner treatment
- Cefixime 400mg PO once PLUS
- Azithromycin 1g PO once OR
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 7 days
Cephalosporin Allergy
- Azithromycin 2g PO once PLUS
- Gentamicin 240mg IM once[4]
- In theory this high dose macrolide will provide treatment for both GC and Chlamydia
Associated Bacterial Vaginosis or Trichomonas vaginalis
Non-Pregnant
- Metronidazole 2g PO once or 500mg PO BID for 7 days
- Tinidazole 2g PO once
Pregnant
- Only treat if the patient is symptomatic and avoid breast feeding until 24hrs after last Metronidazole treatment and 72hrs after Tinidazole
- Metronidazole 2g PO once
Sexual Partner Treatment
- Metronidazole 500mg PO BID x 7 days or Tinidazole 2g PO once
Women with HIV Infection
- Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x 7 days[5]
Epididymitis/Epididymorchitis
- For acute epididymitis likely caused by STI
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose PLUS
- Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 10 days
- For acute epididymitis most likely caused by STI and enteric organisms (MSM)
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose PLUS
- Levofloxacin 500 mg orally once a day for 10 days OR
- Ofloxacin 300 mg orally twice a day for 10 days
- For acute epididymitis most likely caused by enteric organisms
- Levofloxacin 500 mg orally once daily for 10 days OR
- Ofloxacin 300 mg orally twice a day for 10 days
Treat sexual partner if possible
GC/Chlamydia Conjunctivitis
Chlamydial
- Doxycycline 100mg BID for 7 days OR
- Azithromycin 1g (20mg/kg) PO one time dose
- Newborn Treatment: Azithromycin 20mg/kg PO once daily x 3 days
- Disease manifests 5 days post-birth to 2 weeks (late onset)
Gonococcal
- Dual treatment for Chlamydia is recommended with azithromycin
- Ceftriaxone 1g IM one dose PLUS
- Azithromycin 1g PO one dose
- Newborn Treatment:
- Prophylaxis: Erythromycin ophthalmic 0.5% x1
- Disease manifests 1st 5 days post delivery (early onset)
- Treatment Ceftriaxone 25-50mg IV or IM, max 125mg
Herpes
Initial Episode[6]
- Acyclovir OR
- 400mg PO q8hrs x 7-10 days
- or 200mg PO 5x/day x 7-10 days
- Valacyclovir 1g PO q12hrs x 7-10 days OR
- Famciclovir 250mg PO q8hrs x 7-10 days
Recurrence[6]
- Acyclovir OR
- 400mg PO q8hrs x 5 days
- or 800mg PO q12hrs x 5 days
- or 800mg PO q8hrs x 2 days
- Valacyclovir OR
- 500mg PO q12hrs x 3 days
- or 1g PO qd x 5 days
- Famciclovir
- 125mg PO q12hrs for 5 days
- or 1g PO q12hrs for 1 day
- or 500mg PO once, followed by 250mg PO q12hrs for 2 days
Suppressive Therapy[6]
- Acyclovir 400mg PO q12hrs daily OR
- Famciclovir 250mg PO q12hrs daily OR
- Valacyclovir 500mg-1g PO daily (500mg may be less effective)
Lymphogranuloma Venereum
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 21 days (first choice) OR
- Erythromycin 500mg PO QID x 21 days OR
- Preferred for pregnant and lactating females
- Azithromycin 1g PO weekly for 3 weeks OR
- Alternative for pregnant women - poor evidence for this treatment currently
- Tetracycline, Minocycline, or Moxifloxacin (x21 days) are also acceptable alternatives to Doxycycline
- Treat sexual partner
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 7 days OR
- Azithromycin 1gm PO x1
Proctitis
Inflammation of the rectum (distal 10-12cm)
- Ceftriaxone 125mg IM x1 + Doxy 100mg po bid x 7d
PID
- Treat all partners who had sex with patient during previous 60 days prior to symptom onset
Outpatient Options
- Ceftriaxone 250mg IM x1 + doxycycline 100mg PO BID x14d +/- metronidazole 500mg PO BID x14d [7]
- Metronidazole based upon assessment of risk for anaerobes; consider in:
- Pelvic abscess
- Proven or suspected infection w/ Trichomonas or Bacterial Vaginosis
- History of gynecological instrumentation in the preceding 2-3wks
- Metronidazole based upon assessment of risk for anaerobes; consider in:
- Cefoxitin 2 g IM in a single dose and Probenecid, 1 g PO administered concurrently in a single dose[8] + Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 14 days +/- flagyl based on above criteria
Alternative Outpatient Options
- Ceftriaxone 250mg IM x1 + 1 g of azithromycin per week, x 2 weeks[9] +/- flagyl based on above criteria
- A single randomized controlled trial shows that azithromycin is superior to doxycycline even when compliance in taking doxycycline is excellent (98.2% vs 87.5%)[9]
Inpatient
- Cefoxitin 2gm IV q6hr OR cefotetan 2gm IV q12hr) + doxycycline PO or IV 100 mg q12hr OR
- Clindamycin 900mg IV q8h + gentamicin 2mg/kg QD OR
- Ampicillin-sulbactam 3gm IV q6hr + doxycycline 100mg IV/PO q12hr
Syphilis
Early Stage
This is classified as primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis less than one year.
Treatment Options:
- Penicillin G Benzathine 2.4 million units IM x 1
- Repeat dose after 7 days for pregnant patients and HIV infection
- Doxycycline 100mg oral twice daily for 14 days as alternative
Late Stage
Late stage is greater than one year duration, presence of gummas, or cardiovascular disease
Treatment Options:
- Penicillin G Benzathine 2.4 million units IM weekly x 3 weeks
- Doxycycline 100mg oral twice daily for 4 weeks as alternative
Neurosyphilis
There are 3 Major options with none showing greater efficacy than others:
- Penicillin G 3-4 million units IV every 4 hours x 10-14 days
- Penicillin G 24 million units IV infusion 10-14 days
- Penicillin G Procaine2.4 million units IM daily + probenecid 500mg oral every 6 hours for 10-14 days.
- Alternative:
- Ceftriaxone 2gm IV once daily for 10-14 days
- Desensitization to the penicillin allergy is still the preferred method of treatment for patients with early and late stage disease (especially during pregnancy)
Pregnancy
- Penicillin, dosage depends on stage [10]
Trichomonas vaginalis
Non-Pregnant
- Metronidazole 2g PO once or 500mg PO BID for 7 days
- Tinidazole 2g PO once
Pregnant
- Only treat if the patient is symptomatic and avoid breast feeding until 24hrs after last Metronidazole treatment and 72hrs after Tinidazole
- Metronidazole 2g PO once
Sexual Partner Treatment
- Metronidazole 500mg PO BID x 7 days or Tinidazole 2g PO once
Women with HIV Infection
- Metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x 7 days[11]
See Also
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Ulcerative STDs
- Penile diagnoses
- Pelvic pain
- Expedited Partner Therapy
References
- ↑ CDC: STI Fact sheet 2013
- ↑ Workoski KA and Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recommen and Reports. 2015; 64(3):1-140.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 CDC Pregnancy BV Treatment Guidelines.cdc.gov
- ↑ CDC: 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines
- ↑ CDC. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. MMWR Recomm Rep 2010;59(No. RR-12)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Workoski KA and Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recommen and Reports. 2015; 64(3):1-140.
- ↑ Ness RB et al. Effectiveness of inpatient and outpatient treatment strategies for women with pelvic inflammatory disease: results from the Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Evaluation and Clinical Health (PEACH) Randomized Trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002;186:929–37
- ↑ CDC PID Treatment http://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/2010/pid.htm
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Savaris RF. et al. Comparing ceftriaxone plus azithromycin or doxycycline for pelvic inflammatory disease: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Jul;110(1):53-60
- ↑ Mackay G. Chapter 43. Sexually Transmitted Diseases & Pelvic Infections. In:DeCherney AH, Nathan L, Laufer N, Roman AS. eds. CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Obstetrics & Gynecology, 11e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013
- ↑ CDC. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. MMWR Recomm Rep 2010;59(No. RR-12)