Follow-Up of Abnormal Screening Tests
Two case examples of follow-up for abnormal screening tests follow.
Case 1
Cervical cancer screening test results conducted in-clinic come back as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS) and HPV-negative. What is your next step and when is the next cervical cancer screening test due?
For non-pregnant women between 25 and 65 years of age with ASCUS cytology who have not had HPV co-testing already, HPV testing is the preferred next step (high-risk HPV testing only). With a negative HPV test (either on co-test or after cytology), repeat co-testing every three years is recommended. For more information about special populations, including pregnant women and women 21 to 24 years of age, refer to the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) guidelines. [PDF-324KB]
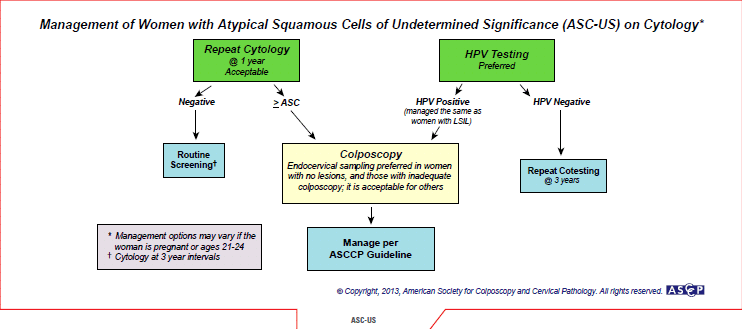
Reprinted from The Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease Volume 17, Number 5, with the permission of ASCCP. © American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology 2013. No copies of the algorithms may be made without the prior consent of ASCCP.
Case 2
A 31-year-old patient’s cervical cancer screening test results come back as cytology negative and HPV-positive. What is your next step and when is the next cervical cancer screening test due?
Follow ASCCP guidance: repeat co-test in one year or do HPV DNA typing now.
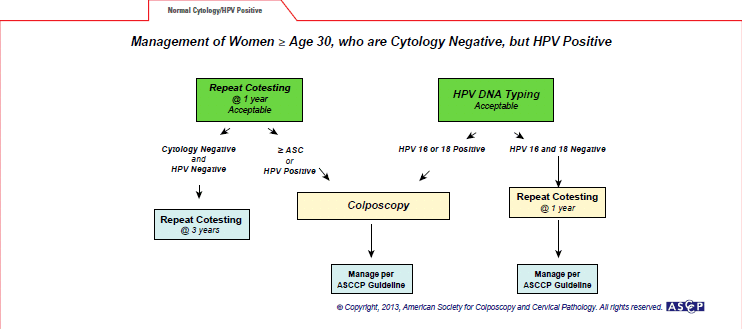
Reprinted from The Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease Volume 17, Number 5, with the permission of ASCCP. © American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology 2013. No copies of the algorithms may be made without the prior consent of ASCCP.
Summary of Cervical Cancer Screening Results and Management for Women 30 Years of Age or Older
| Test Results | What to Do Next |
|---|---|
| Normal Pap and Negative HPV | Rescreen in 5 years. |
| Normal Pap and Positive HPV | Repeat co-test in one year or do HPV DNA typing now (see ASCCP guidelines above). |
| ASCUS Pap, No HPV Test | Repeat cytology in one year or do HPV test now (see ASCCP guidelines above). |
| ASCUS Pap and Negative HPV LSIL Pap and Negative HPV |
Repeat Pap and co-test at interval as per ASCCP guidelines. |
| ASCUS Pap and Positive HPV LSIL Pap and Positive or Unknown HPV ASC-H Pap HSIL Pap |
Colposcopy and/or referral to gynecologist. |
Acronyms
ASCUS = Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance
HSIL = High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions
LSIL = Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions
ASC-H = Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HSIL
- Page last reviewed: September 14, 2015
- Page last updated: September 14, 2015
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir